Prolapse and prolapse of female genital organs
A delicate but extremely relevant problem for many women is prolapse or prolapse of female genital organs. Often it remains unnoticed until the symptoms begin to significantly worsen the quality of life. Discomfort when walking, difficulty urinating, a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen - all this can signal prolapse of the uterus and vagina. Such symptoms do not just interfere with daily activities - they can provoke more serious complications if you do not visit a doctor in a timely manner. Many women face this problem after the birth of a child, the cessation of menstruation, or as a result of excessive physical exertion. It is important to understand that prolapse of the walls of the uterus and vagina is not a common sign of age-related changes, but a condition that can and should be treated.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Causes of prolapse and uterine and vaginal prolapse
The problem can develop over the years, accumulating under the influence of various factors, including lifestyle, physiological nuances and past illnesses. Here are the main reasons leading to this pathology:
- Decreased tone of the muscles and ligaments located in the pelvic floor. With age, the tissues lose elasticity, which makes them less able to hold the uterus and vagina. Regular weight lifting or physical exercise can also harm the muscles
- Postpartum injuries. Difficult or multiple births significantly increase the risk of vaginal prolapse. During childbirth, muscle tissue and ligaments can stretch or tear. Women whose fetus is of an impressive size or whose labor lasts too long experience particular stress.
- Hormonal changes. A decrease in the amount of estrogen during menopause leads to a deterioration in the quality of tissues. They become less elastic, which can provoke the occurrence of prolapse.
- Genetic predisposition. Some women have weak connective tissues from birth, or an abnormal structure of the pelvic floor. All this can make the risk of developing prolapse of the walls of the uterus and vagina higher.
- Lack of physical activity. A sedentary lifestyle can lead to a decrease in the tone of the tissues that hold the internal organs. Lack of movement is just as harmful as excessive stress.
- Chronic factors that make intra-abdominal pressure excessively high. This problem overloads the pelvic floor, causing prolapse of the uterine and vaginal walls. The following pathologies can be dangerous:
- Constant constipation
- Chronic cough (lung diseases, smoking, etc.)
- Excess body weight, which creates additional stress on the tissues
Gynecological or abdominal surgeries can disrupt the anatomical structure of the organs located in the pelvis. For example, removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) sometimes causes displacement of other organs.
Treatment of uterine prolapse
Surgical treatment
The main method of combating moderate and severe prolapse is surgery. Doctors perform several types of operations:
- Colporrhaphy (suturing the vaginal walls). The method is used if prolapse is associated with weakening of the vaginal walls. The doctor sutures one of the vaginal walls, restoring its shape and preventing further prolapse of organs. The operation is performed under general or spinal anesthesia through the vagina. Rehabilitation takes 4-6 weeks
- Fixation of the uterus to the sacral ligament or other structures. With this technique, the uterus is fixed to the bone or ligament structures of the pelvis using special suture materials or mesh implants. The operation can be performed laparoscopically (through small punctures) or through the vagina. Rehabilitation is less traumatic, recovery takes 2-4 weeks
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus). In case of severe prolapse and no plans for pregnancy, the uterus can be removed. This method is often combined with fixation of other organs to prevent their displacement. The operation is performed through the vagina or using laparoscopy. A full return to active life is possible in 6-8 weeks
In the early stages of prolapse, non-surgical methods are suitable for patients. This is also true for women for whom surgical intervention is contraindicated. If there are indications for it, you can find out the price of uterine prolapse surgery in Moscow by calling the clinic "K+31".
Conservative therapy
Non-surgical methods for combating the displacement of pelvic organs:
- Exercises aimed at strengthening the pelvic floor muscles (Kegel method). Regular exercise helps to tone the muscles that support the walls of the uterus. Exercises include successive tension and relaxation of the pelvic floor muscles, similar to that used to stop urination. Noticeable results appear after 2-3 months of regular exercise.
- Pessaries (vaginal rings). These are medical devices that are inserted into the vagina to maintain the organs in the correct position. Pessaries are selected individually and installed by a doctor. They need to be removed and treated regularly.
- Hormonal therapy. It is used during menopause to improve the condition of the pelvic floor tissues. Estrogens help increase their elasticity and reduce the risk of prolapse progression. Application form: ointments, suppositories or tablets
However, there are other methods.
Laser therapy
The technique is a modern non-invasive method aimed at stimulating the production of collagen in the vaginal tissues. This improves the elasticity of its walls and increases the overall tone. The procedure is performed on an outpatient basis, takes 20-30 minutes and does not require anesthesia. During the session, the laser beam affects the mucous membrane, activating cell regeneration and enhancing their ability to support the surrounding organs.
The patient can return to normal life immediately after the session, since there is no rehabilitation period. Laser treatment of vaginal wall prolapse is comfortable, does not cause pain and has no pronounced side effects. However, the technique is effective only in the initial stages of prolapse, when the tissues are still able to respond to stimulating effects.
Physiotherapy
Involves the use of devices for electrical stimulation of the pelvic floor muscles. The technique is based on the gentle effect of electrical impulses that cause the muscles to contract, which helps to strengthen them and restore their tone. These procedures are carried out in specialized clinics under the supervision of medical personnel. One course usually includes 10 to 15 sessions, each lasting about 30-40 minutes.
The procedure is painless, but during stimulation a slight tingling or warmth sensation is possible. Physiotherapy is especially effective in combination with pelvic floor exercises, as it complements their effect and accelerates the recovery process.
After completing a course of physiotherapy, patients often note a decrease in symptoms of vaginal wall displacement and uterine prolapse, improved urinary control and an overall increase in comfort.
Peculiarities
- Who are experiencing menopause
- Who have suffered birth injuries, multiple births
- Who have undergone surgeries involving the removal of 2 ovaries
Genital prolapse is a problem that is successfully eliminated by gynecology specialists at the K+31 Clinic. If symptoms occur that indicate the development of such a pathology, urgently consult a doctor to promptly identify the problem and eliminate it immediately, without waiting for the worst consequences.

Answers to popular questions
Frequently asked questions are answered by doctors from the K+31 clinic.
Is it possible to completely cure uterine prolapse without surgery?
Is the insertion of a pessary painful, and can it be used continuously?
Do Kegel exercises help in the later stages of prolapse?
Can uterine prolapse be prevented?
Does prolapse affect sexual life?

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
Hormone therapy
Radio wave gynecology with the Surgitron deviceLaser therapy using the Photona device
Sling operations Ectopic pregnancy Delayed menstruation Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) Thrush (vaginal candidiasis) Prolapse of the uterus and vagina Uterine polyp (endometrial polyp) Cervical dysplasia Adenomyosis Treatment of sexual infections Vaginitis (Colpitis) Erythroplakia of the cervix Endometritis Bacterial vaginosis Symphysitis (symphysiopathy) Erosion and ectopia of the cervix Vulvovaginitis Premenopause Uterine artery embolization for uterine fibroids Cervicitis Gynecologist consultation Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) Amenorrhea Removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) Postmenopausal Sphinctermetry Treatment and intimate rejuvenation with the Fotona laser Adenomyosis (Endometriosis of the uterus) Vulvitis Vaginal surgeries Inflammation of the appendages (adnexitis, salpingo-oophoritis) Labiaplasty (labiaplasty) Bartholinitis Surgery to remove an ovarian cyst Prolapse (prolapse) of the uterus and vagina Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) First menstruation 7 days after embryo transfer Biochemical pregnancy IVF protein diet Day 5 after embryo transfer Follicles Bicornuate uterus and pregnancy Day 9 after embryo transfer 1 day after embryo transfer Age and Fertility 10 days after embryo transfer

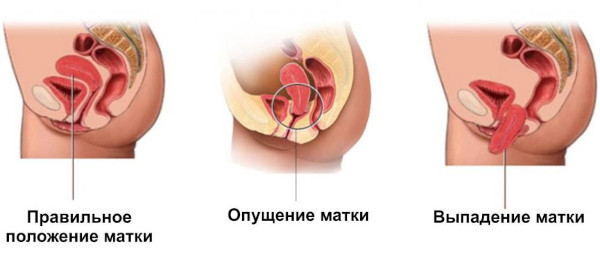







































Symptoms of uterine prolapse
Typical signs of this condition:
Against the background of physical symptoms, many women develop emotional problems: a sense of shame, decreased self-esteem, fear of intimacy.