Ovarian diseases
Ovaries are paired organs of the reproductive system that are responsible for the production of eggs and hormones. Disruptions in their work often occur due to hormonal imbalances and inflammatory processes. In this article, we will consider in detail the main types of ovarian diseases, their symptoms and treatment methods.

specialists

equipment

treatment

About the service
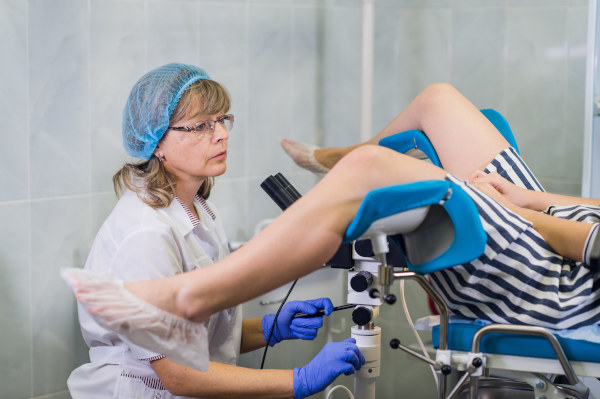
To diagnose ovarian diseases, standard blood and urine tests, bacterial culture are prescribed. The patient must undergo a gynecological examination and ultrasound.
Follicular neoplasms are subject to observation. Surgical treatment is necessary only in cases where, over the course of two months, against the background of conservative therapy (hormones are prescribed, usually in the form of oral contraceptives), the cyst does not decrease, but continues to grow. Surgery is also resorted to in case of torsion of the pedicle or rupture of the neoplasm.
Modern operations are minimally invasive. They are performed through laparoscopic access using endovideosurgical instruments. This allows to reduce the rehabilitation period, scars are practically invisible on the skin after healing. If there are no complications after the operation, then the patient is discharged from the hospital after 3-6 days.
The following types of surgeries are performed on the ovaries:
- Cystectomy (the surgeon performs enucleation of the cyst).
- Ovariectomy (complete removal of the ovary).
Types of ovarian diseases

The most common ovarian diseases include:
- Ovarian inflammation (oophoritis)
- Ovarian cyst
- Polycystic ovary disease
- Cancer
Against the background of hormonal imbalance, infections, complicated childbirth, abortions, women also face ovarian endometriosis. If left untreated, it threatens infertility and chronic pelvic pain.
Ovarian diseases are most often detected during a routine gynecological examination, so you should not neglect regular visits to the doctor. After all, the earlier the disease is diagnosed, the higher the chance of a full recovery without negative consequences for health. The primary symptoms that should alert you include:
- Slight pulling in the lower abdomen
- Short-term pain in the area of the ovaries
- Urinary or bowel dysfunction
Inflammation of the ovaries
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation
Oophoritis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Drawing or sharp pains in the lower abdomen, which intensify with physical activity, during menstruation
- Irregularities in the menstrual cycle - periods become irregular, too heavy or scanty
- Abnormal vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor, an admixture of pus
- An increase in body temperature to 37.1–38 °C, severe fever
- General weakness, loss of strength, rapid fatigue, decreased performance
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Frequent urge to urinate, pain and burning
Oophoritis rarely goes away on its own. Without treatment, there is a high probability of adhesions in the pelvis and chronic pain.
Treatment of ovarian inflammation
Treatment of ovarian inflammation is aimed at eliminating the infectious process, relieving inflammation, and preventing possible complications. It includes:
- Antibacterial drugs. In most cases, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed - cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Ibuprofen and diclofenac are used to reduce inflammation and swelling, relieve pain
- Drugs to strengthen the immune system. Immunomodulators are indicated for chronic diseases. They increase the body's defenses, helping it fight infection more effectively
- Physiotherapy. After eliminating the acute inflammatory process, it is recommended to undergo a course of electrophoresis, magnetic therapy or ultrasound. The procedures improve blood circulation in the pelvis and accelerate the process of tissue restoration
- Vitamin therapy. Necessary to support the body during the treatment and recovery period. Includes complexes containing vitamins of group B, C and E
An important aspect during treatment is proper nutrition and giving up bad habits. The doctor of the clinic "K+31" recommends excluding fatty, spicy and heavy foods, eating more vegetables, fruits and foods rich in protein.
In the presence of complications, for example, purulent formations in the ovaries, surgical treatment is required. To eliminate the source of inflammation, a minimally invasive procedure is performed - laparoscopy.

Ovarian and appendage cysts
Ovarian and appendage cysts are benign formations filled with fluid or other contents. They occur both on the surface and inside the ovary. There are 2 types:
- Functional - appear during the work of the ovary
- Pathological - associated with disturbances in the structure of tissues
Functional cysts include follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. They disappear on their own within a few menstrual cycles. Pathological dermoid or endometrioid cysts require more careful monitoring or treatment.
According to statistics, up to 20% of women of reproductive age are faced with functional cysts. Pathological forms of cysts are detected in 10-15% of patients.
In postmenopause, the likelihood of cysts is significantly lower, but the risk of malignant changes increases. Early detection of cysts helps to avoid rupture, torsion of the pedicle, and the development of inflammatory processes.
Symptoms of ovarian and adnexal cysts
Symptoms of ovarian and adnexal cysts:
- Drawing pain in the lower abdomen on one or both sides, which intensifies during exercise, intimacy, menstruation
- Menstrual irregularities - delays, excessively heavy discharge, severe pain
- A feeling of pressure - large formations press on adjacent organs, causing a feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Irregularities in urination, defecation - a large cyst compresses the bladder or intestines
- Abdominal bloating associated with cyst growth or fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity
When the cyst stalk is twisted or ruptured, acute pain occurs, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and fever.
Treatment of ovarian and appendage cysts
The approach to treating ovarian cysts in women depends on the type of cyst, its size, symptoms, and risk of complications. The main methods include:
- Observation. Functional cysts often do not require treatment. The doctor recommends repeating the ultrasound in 2-3 months to monitor their condition
- Drug therapy. To regulate hormonal levels and prevent new formations, hormonal contraceptives, anti-inflammatory drugs, and painkillers are prescribed to relieve pain.
- Surgical treatment. In the presence of large cysts, suspicion of their malignant nature, or the occurrence of complications, laparoscopy is performed.
- Physiotherapy. After surgical treatment, to speed up recovery, it is recommended to undergo a course of electrophoresis, magnetic therapy
Untreated cysts can lead to serious consequences, including rupture, infertility or malignant degeneration.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price