Delayed menstruation

specialists

equipment

treatment
How does the menstrual cycle proceed?
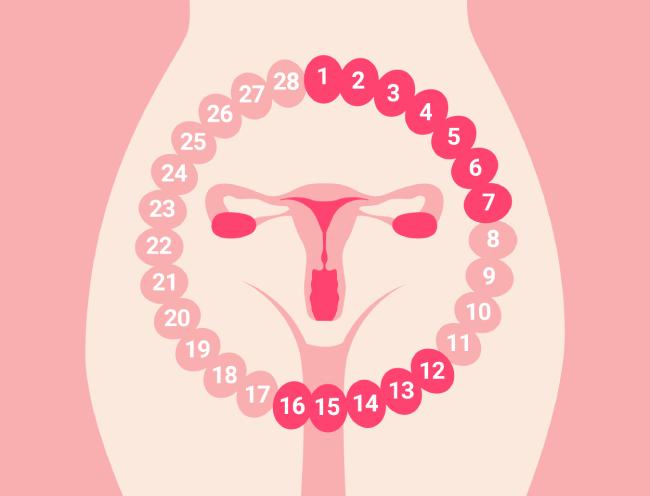
Menstruation is a sequential hormonal process, the purpose of which is to prepare the body for possible conception. On average, its duration is 28 days, but deviations within 21–35 days are also considered normal. The whole process is divided into three stages:
- Preparation of the follicle. With the onset of bleeding, follicle development begins in the ovaries. The hormone estrogen helps restore the inner layer of the uterus
- Release of the egg. Around the middle of the period, one follicle ruptures and the egg passes into the fallopian tube, where it is ready to fuse with a sperm. This process lasts only a day
- Final stage. After ovulation, a temporary gland is formed, responsible for the production of progesterone, which is needed to prepare the uterus for a possible pregnancy. If a new life is not born, this hormone decreases and the cycle begins again
Normally, this process takes 28 days. If there is no pregnancy, the next cycle begins.
Reasons for missed periods
1. Pregnancy
Delayed menstruation is the first sign that you pay attention to when you suspect pregnancy. After fertilization of the egg and its attachment to the wall of the uterus, the woman’s hormonal background changes. Progesterone levels increase, which prevents endometrial rejection and the onset of menstruation.
To confirm pregnancy, you can do a test for the presence of the hormone hCG in the urine. For a more accurate result, it is better to get tested by a doctor.
2. Stress and loads
Strong emotional stress can cause a temporary disruption of the cycle. The body turns on a protective mechanism: stress causes changes in the functioning of the hypothalamus, which affects the production of hormones that regulate the arrival of menstruation. Severe physical stress, especially in female athletes, can also contribute to the delay.
3. Sudden changes in body weight
A decrease in body weight below a critical level (less than 45 kg or a deficiency of adipose tissue) can cause the synthesis of certain hormones to stop. The body, being in “economy mode,” stops processes associated with reproduction, which is reflected in a delay in menstruation. Rapid weight gain, especially with obesity, provokes hormonal imbalance, which also affects the cycle.
4. Hormonal contraceptives
Oral medications and intrauterine devices (IUDs) containing hormones affect ovulation and your cycle. While a woman adapts to the pills or when she cancels them, disturbances are possible, since the body needs time to restore its natural hormonal levels.
Sometimes a delay in menstruation can be associated with improper use of pills, which, among other things, can lead to pregnancy, so it is important to strictly follow the instructions and consult a doctor.
5. Lactation period
Breastfeeding has a significant impact on the female body, including the menstrual rhythm. This is due to increased levels of prolactin, a hormone that promotes milk production after pregnancy and childbirth. Prolactin also blocks ovulation, which leads to a temporary suspension of menstruation. In women who are breastfeeding, menstruation may not return for several months or may be irregular.
6. Endocrine disorders
Failures in the hormonal system can change the rhythm of menstruation. The most common reasons include:
- Pathologies in the thyroid gland
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
To identify endocrine disorders, the patient is prescribed tests that are carried out in a laboratory (hormonal profile) and diagnostics of the pelvic organs using ultrasound.
7. Age-related changes
Cycle disruptions in women over 45 years of age can often indicate a transition period called perimenopause. The period may be characterized by a decrease in estrogen synthesis, which leads to an atypical frequency and volume of menstruation for the patient. Gradually, the likelihood of pregnancy decreases as much as possible, and menopause occurs.
If such changes occur before the age of 40, this may indicate premature ovarian failure. In such cases, it is recommended to consult a doctor to rule out pathological processes and discuss possible options for hormonal support.
8. Effects of drugs
Certain medications can disrupt the regularity of your periods. These include hormonal drugs, antidepressants, drugs that regulate blood pressure or prescribed for cancer.
9. Gynecological diseases
Pathologies of the reproductive organs are one of the common causes of delayed menstruation. For example:
- Endometriosis. Endometrial pathologies often cause cycle disruption and pain
- Uterine fibroids. A benign tumor, sometimes accompanied by irregular or heavy periods
- Inflammation. Infections that can be spread sexually (chlamydia, gonorrhea) can cause disorders
To diagnose the condition, tests, gynecological examination and ultrasound are required.
10. Other factors
Some of the less obvious reasons for missing periods include:
- Change of climate or time zone
- Chronic diseases (for example, diabetes)
- Long or frequent air travel
- Poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency
If menstrual delays occur regularly or are accompanied by any unpleasant symptoms (pain, bleeding), you should immediately visit a doctor to determine the cause of the problem and develop treatment tactics.
Answers to popular questions
Gynecologists at the K+31 clinic answer
What is the norm for days of late menstruation?
The permissible delay in menstruation in the absence of pregnancy and any visible reasons is from 3 to 7 days. The cycle may be temporarily disrupted due to stress, climate change or physical activity. However, if the disturbance exceeds 7 days or becomes regular, a visit to the doctor is necessary.
What to do if your period does not start on time?
First of all, rule out pregnancy by taking a test. If the result is negative and the delay continues, analyze recent events: stress, diet, medication. If your period does not come after 10 days, it is important to consult a gynecologist.
Could a missed period be associated with night shifts?
Yes, working night shifts disrupts the production of melatonin, a hormone that affects the hypothalamus. A chaotic schedule can lead to temporary amenorrhea (lack of menstruation). The solution is to try to maintain a consistent sleep pattern, even when working at night.
What should you do if your cycle is restored, but your periods become painful?
Sometimes restoration of the cycle after a delay is accompanied by dysmenorrhea (painful periods). This may be due to increased work of the uterus or temporary inflammation. It is best to consult your doctor to rule out endometriosis or other problems.
Could a delay be a sign of early menopause?
If you are under 40 years old, but your periods become regular and are accompanied by hot flashes, irritability or decreased libido, this may indicate ovarian insufficiency.
Do I need to take hormones to “return” my cycle?
Hormonal therapy is prescribed only as prescribed by a doctor. Sometimes the cycle is restored naturally - it is enough to eliminate the cause of the failure.
Could cycle changes be related to genetics?
Yes, features of the menstrual cycle can be inherited. For example, delays in the absence of pregnancy or early menopause in women in your family may be due to genetic factors.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services





















































What is a missed period?
If bleeding does not occur on time, it is said to be delayed. For most women, the cycle varies from 21 to 35 days, but this time frame varies from person to person. A missed period during pregnancy is normal. If, in its absence, menstruation is delayed for 5–7 days or more, this may indicate a violation. A small or large delay in menstruation can be associated with both natural causes and pathological changes.