Tumor diseases of the pelvic organs

specialists

equipment

treatment
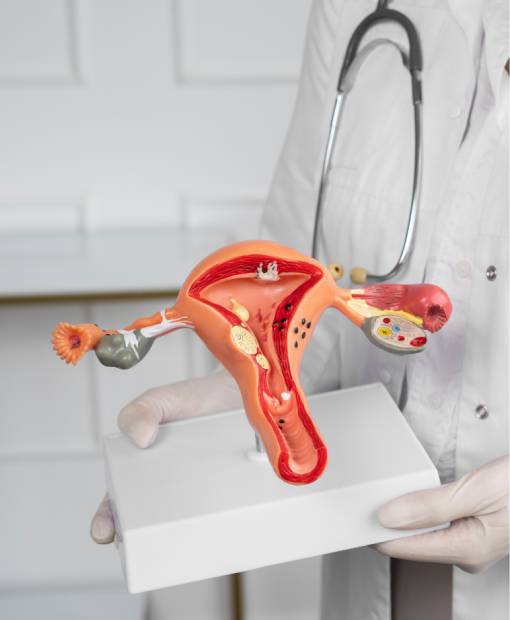
About the disease
The treatment regimen for pelvic tumors is developed by the doctor individually in each case. It depends on various factors:
- Type of neoplasm
- Presence of concomitant diseases, complications
- Location of education
- Stages of the disease
- Causes of occurrence
- What type of tumor (benign, malignant)
- Patient’s age and body characteristics
If possible, resort to conservative treatment with drugs. Surgery is indicated if there is heavy bleeding due to tumor rupture, it is large, or it is growing very quickly. In these cases, surgical treatment is indicated, which consists of removing the tumor.
The scope of surgical intervention also differs. Most often they resort to organ-preserving operations. For example, this is possible with ovarian cysts. Radical amputation may be indicated for large fibroids or if a malignant neoplasm is detected, when it is better to remove the entire organ.
In parallel with surgery, antibacterial or antiviral therapy can be carried out. The doctor often prescribes medications to the patient to stimulate the immune system. The use of various methods allows you to speed up recovery, avoid the development of concomitant diseases and significantly reduce the duration of the recovery period.
To avoid complications and surgery, it is necessary to undergo routine gynecological examinations in a timely manner and at the first symptoms of diseases of the reproductive system, immediately contact your doctor. Timely diagnosis and properly selected treatment at the K+31 medical centers in Moscow significantly improves the prognosis for a full recovery.
A tumor in the pelvis in women is most often detected during a routine gynecological examination. They are divided into benign and malignant tumors of the female organs. Most often neoplasms can be found in the organs of the reproductive system: uterus, ovaries, cervix. But they can also occur in the peritoneum, affecting the intestines and bladder (localization in the abdominal cavity is somewhat less common). Neoplasms in the pelvis can also affect the bones.
Among the reasons for the development of neoplasms:
- Hereditary predisposition
- Irradiation (ultraviolet or radiation during radiation therapy) that led to the development radiation sickness and, as a consequence, the appearance of malignant pelvic tumors in women
- Viruses and infections (including HPV)
- Pathologies of the endocrine system that lead to hormonal imbalances (for example, lack of female hormones)
- Chemicals that can cause DNA damage
- Mechanical injuries and hypothermia
- Thyroid gland malfunctions (hormone-dependent tumors, for example, ovarian cyst)
- Deterioration of the general condition of the immune system
Other services

Appointment to the doctor
A formation in the pelvis in women can form at different ages. Sometimes a tumor occurs in girls during puberty in the early stages of the cycle. This is due to the accumulation menstrual fluid in the vaginal cavity and disruption of its outflow processes. The cause of the development of pathology depending on the location, there are congenital malformations of the cervix or vagina or atresia (infestation) of the hymen.
Women of reproductive age most often develop fibroids. It is a benign neoplasm of smooth muscle origin.
During a gynecological examination of the pelvis, women may be diagnosed with Graafian vesicles. In medicine they are also called functional ovarian cysts. In most cases they don't grow and do not require treatment, as they go away on their own within a few months.
Among other types of neoplasms, ectopic pregnancy should be noted (attachment of the fertilized egg to the fallopian tubes, cervix, etc.), ovarian cancer, malignant formations on the walls of the fallopian tubes. Cystic teratoma and hydrosalpinx are also common. In the presence of multiple neoplasms in the ovaries, provided that these are benign tumors or when the inner layer of the uterus grows, a diagnosis of endometriosis is made.
During the postmenopausal period, malignant neoplasms are more often diagnosed. This is due to the fact that cysts fibroids or endometriosis are usually associated with hormonal secretion from the ovaries. During postmenopause it drops significantly.
In any case, it is important to undergo regular examinations so as not to miss the moment the appearance of pelvic cancer, which is much more dangerous than a benign neoplasm.
When collecting anamnesis, the doctor may pay attention to endocrine disorders and disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. tract. After excluding pathologies of these systems, a full gynecological examination is performed, Ultrasound, bimanual examination of the vagina (palpation), endoscopic examination, biopsy and/or hysteroscopy (examination using an optical instrument). It is important to note that when there are symptoms of a small tumor pelvis, ultrasound examination is not always enough and the listed methods, as a rule, are added to them clinical studies such as:
- Blood and urine tests
- CT and MRI
When there are signs of malignant pelvic tumors, the doctor takes a tissue biopsy for examination cells and exclude or confirm the patient’s oncological status. They also conduct an examination located next to the neoplasm of lymph nodes, if the tumor is malignant, this helps to determine whether the cancer has spread further or not. Tumor markers may be required.
Common symptoms indicating for the presence of a neoplasm in the pelvic area:
Price
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.




































