Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer (female reproductive glands) is a malignant tumor that develops in the ovaries and affects their tissue. Like other forms of cancer, ovarian cancer is a serious and dangerous disease.

specialists

equipment

treatment
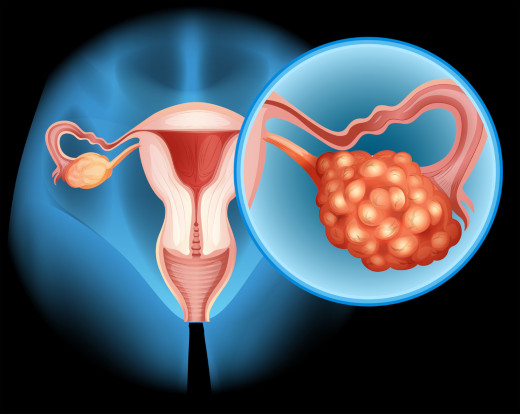
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The causes of ovarian cancer are not yet fully understood, but risk factors that may influence the appearance of a malignant tumor include the following:
- Genetic predisposition. If you have a relative who has been diagnosed with ovarian cancer or breast cancer, this increases your risk. Mutations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes are responsible for this.
- The period of the beginning and end of menstruation. It is believed that early onset of menstruation and late onset of menopause in a woman increases the likelihood of developing ovarian cancer
The risk of developing a malignant ovarian tumor increases to a lesser extent in the presence of the following factors:
- Age over 50
- Taking hormones, oral contraceptives
- Tubal ligation
- Breastfeeding
The development of ovarian cancer can also be provoked by inflammatory processes in the pelvic organs, STDs, and hormonal disorders.
Types of ovarian cancer
By origin, malignant ovarian tumors can be divided into:
Primary tumors - they form in the cells of the ovary. The most common type of primary ovarian cancer is carcinoma - a tumor that forms due to gene mutations in epithelial cells. Carcinomas can be divided into:
- Serous – most common, in about half of cases
- Endometrioid – 10% of ovarian cancer cases
- Mucinous – 6% of cases
- Clear cell carcinoma – also 6%
Ovarian cancer less often develops in germ cells (germ cell tumors) or stromal cells (stromal tumors)
Secondary – these are metastases of oncological diseases of other organs that have entered the ovaries with blood or lymph.
Stages of ovarian cancer
The most common classification of ovarian cancer stages distinguishes four stages of its development:
- the tumor does not extend beyond the ovary
- cancer affects adjacent organs and tissues of the pelvis
- ovarian cancer metastasizes to abdominal organs and nearby (regional) lymph nodes
- there are distant metastases in other organs and tissues of the body
What do we treat
Thyroid diseases
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other cancer treatment services
Hormone therapy
Check-up Immunotherapy Palliative care Orthopedic rehabilitation Cancer council Oncologist appointment Prevention of hair loss during chemotherapyRobotic surgery
Targeted therapy Genetic tests for cancer Biopsy under ultrasound guidance Second opinion in oncology Chemotherapy Endocrine therapy




















































Symptoms of Ovarian Cancer
In the early stages, ovarian cancer is usually asymptomatic. Early signs of malignant tumors may not cause any particular problems for a woman and may not attract her attention. Unfortunately, symptoms that begin to bother her appear in the later stages of ovarian cancer (stages 3 or 4). The most common symptoms of this oncological disease are:
Pain in the lower abdomen and/or back. They may not be strong, aching, usually one-sided, with long periods of calm. The pain may be accompanied by a feeling of heaviness in the lower abdomen, the appearance of harder areas in it.
Changes in the functioning of the bladder (frequent urge to urinate) and intestines. This is due to the fact that ovarian tumors press on the bladder and/or rectum, which manifests itself in constipation and frequent urination, a feeling of incomplete emptying.
Enlargement of the abdomen due to ovarian tumors and their metastases in the peritoneum and other pelvic organs. Neoplasms lead to the accumulation of fluid (ascites) in the abdominal cavity. This condition worsens well-being, shortness of breath and loss of appetite may occur.
In the last stages of ovarian cancer, symptoms characteristic of any oncology appear: weight loss, exhaustion, weakness, etc.
If there are any signs of ovarian cancer, you need to urgently undergo an examination by an oncologist-gynecologist, since the prognosis for treating an advanced disease is very pessimistic.