Follicles
Even during intrauterine development, the body of girls begins to form more than 500,000 follicles. Upon reaching puberty, the reproductive system contains about 40,000 such structures. During life, no more than 500 eggs fully mature, and the remaining microscopic oocyte rudiments undergo atresia.

specialists

equipment

treatment
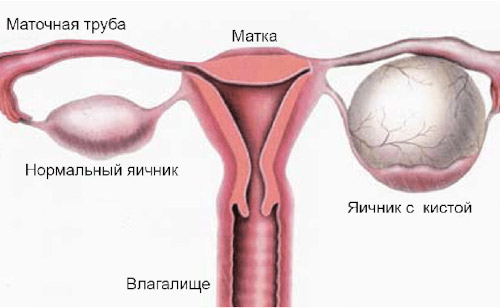
Follicles in the ovaries
Inside the ovaries, oocytes mature, ready for fertilization by sperm. Conception is possible only in the case of their full development and maturation. Hormonal imbalances often lead to the appearance of deviations that provoke the formation of cysts or infertility.
The main task of the follicle is to protect oocytes from destruction and the negative influence of endogenous factors. The eggs located in the female gonads are not yet mature. That is why the success of conception and the course of pregnancy largely depend on the degree of protection of the oocytes from the influence of destructive factors.
Follicles grow poorly
Underdevelopment of the structural components of the ovaries is one of the main causes of female infertility. In the absence of a dominant follicle, luteinizing hormones that stimulate ovulation do not enter the blood. The main causes of insufficient development of germ cells include:
- Hypothalamus pathologies
- Dysfunction of the ovaries
- Contraceptive abuse
- Consequences of infection in the small genital organs
- Thyroid pathologies
- Endocrine disorders
- Depression and emotional instability
- Formation of tumors in the pituitary gland
Adequate hormonal therapy allows you to restore the menstrual cycle and the process of oocyte maturation. If conservative treatment is ineffective, ovarian cauterization is prescribed, which involves surgical removal of underdeveloped cells from the sex glands.
Stages of follicle development

Folliculogenesis is the continuous maturation of follicles, which begins in the antenatal period and ends in the climacteric period. Due to apoptosis, most immature female germ cells die. Only a small part of them goes through the entire maturation cycle and takes part in ovulation.
The types of structural elements of the ovaries are determined by the stage of their development:
- Primordial (embryonic)
- Preantral (primary)
- Antral (secondary)
- Preovulatory (Graafian follicles)
24 hours before ovulation, the production of estrogen increases, stimulating the flow of luteinizing hormone into the blood. It is the peptide hormones that initiate the formation of a protrusion in the follicular sac, from which the oocyte subsequently emerges (ovulation).
Follicle cycle

Throughout the menstrual cycle, changes occur in a woman's reproductive system that precede ovulation. The size and location of the follicular sacs are determined by the phases of this cycle:
- Menstrual (duration 3-6 days) - bleeding from the uterus caused by the rejection of the endometrium
- Follicular (duration 14 days) - the process of development of new structural elements of the ovaries, which begins with the production of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones that accelerate their growth
- Ovulatory (duration 3 days) - rupture of the dominant follicle with the subsequent release of the oocyte ready for fertilization
- Luteal (duration 16 days) - intensive production of progesterone and estrogen, preparing the female body for pregnancy
Mature oocytes are visible to the naked eye on the screen of the ultrasound scanner. Normally, 1 to 3 dominant follicles mature during one menstrual cycle.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services














































What does follicle mean?
A follicle is a structural element of the female reproductive glands, which consists of an oocyte surrounded by a layer of connective and epithelial tissue. It contains only one 1st order egg cell, inside of which there is a small nucleus - the "germinal vesicle".
The oocyte (egg cell) is enclosed in a dense glycoprotein capsule surrounded by granulosa cells. Their surface is covered with a thin acellular layer of matrix, around which the theca cell is located.