Uterine polyp (endometrial polyp)
Uterine endometrial polyp is a problem that cannot be ignored. Unpredictable bleeding, pain, a feeling that something is wrong with the body - all this is frightening and raises questions. Why did this happen? How dangerous is it? What to do next? If you are faced with such experiences, it is important to remember: a polyp is a condition that can be treated. In this article, we will explain in simple terms where it comes from, what it threatens, and how to regain your comfort and peace of mind.

specialists

equipment

treatment

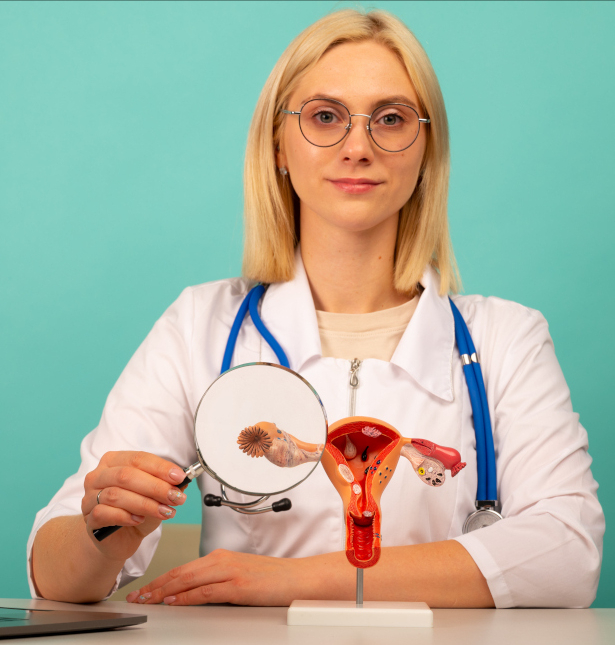
What is an endometrial polyp?
An endometrial polyp is a growth that appears on the inner lining of the uterus. Imagine that the endometrial tissue, which is renewed every cycle, begins to grow too actively in one place. As a result, a small growth is formed, resembling a nodule or appendage.
Uterine polyps come in different sizes: from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters. They can be single or multiple. Most often, neoplasms do not pose a serious threat, but they still cause a lot of concern.
The main problem with endometrial polyps is their unpredictability. Sometimes they do not manifest themselves in any way, and sometimes they become the culprit of irregular bleeding, pain, or difficulties with conception. The reasons for their appearance can be different: hormonal imbalance, inflammatory processes, uterine trauma after childbirth, or surgery.

Uterine adenoma may not show any symptoms for a long time, but in some cases it becomes the cause of noticeable symptoms that interfere with living a normal life.
Most often, women experience the following symptoms:
- Irregular bleeding, including spotting between periods
- Heavy or prolonged periods that used to be normal
- Lower abdominal pain, pulling or cramping
- Bleeding or discomfort after intercourse
- Difficulty conceiving if the formation interferes with embryo attachment
Polyps, especially large ones, sometimes cause a feeling of pressure in the pelvic area or a feeling of "fullness".
Important! In women during menopause, bleeding of any nature should be a reason for urgent consultation with a doctor.
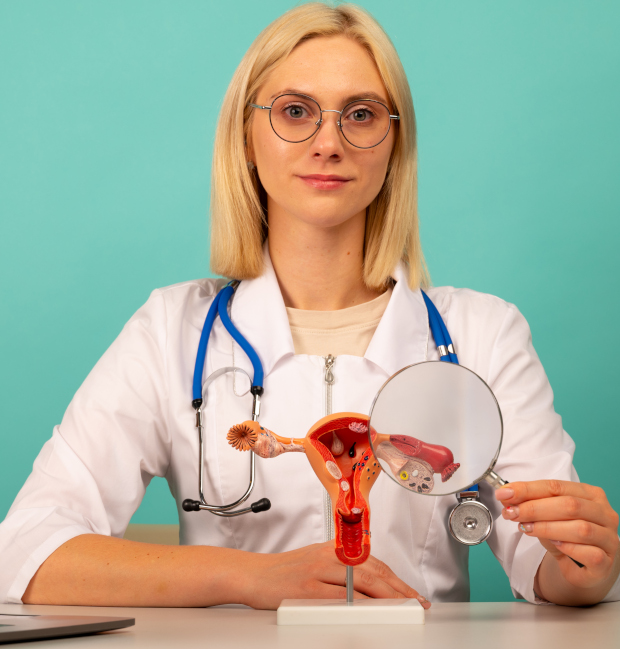

Endometrial neoplasms of the uterus do not just appear. Their appearance is associated with changes in the body, especially in the hormonal system.
The main factors in the formation of adenoma:
- Hormonal disruptions. If the level of estrogens (hormones that affect the growth of the endometrium) is increased, the tissues of the uterus begin to grow too actively, which leads to the formation of adenoma
- Inflammatory processes. Chronic inflammation in the uterus or appendages creates a favorable environment for pathological tissue proliferation
- Mechanical injuries. Damage to the uterine mucosa, for example, after abortions, curettage or childbirth, can become a trigger for the development of neoplasms
- Metabolic disorders. Excess weight or diabetes also affect hormonal balance and increase the likelihood of adenoma.
Neoplasms often occur in women during periods of hormonal changes, for example, after 40 years, in premenopause. This is due to a natural change in hormone levels, which affects the tissues of the uterus.
In addition, risk factors include the use of certain hormonal drugs, such as tamoxifen, which is used to treat tumors.
Types of uterine polyps
The neoplasms can be single, but sometimes they form in groups. Such multiple adenomas are called endometrial polyposis.
The size of neoplasms of the uterine endometrium varies from several millimeters to several centimeters. Small adenomas often do not manifest themselves in any way, and large ones can cause bleeding, pain or pressure on neighboring organs.
The main types of polyps of the uterine endometrium:
-
Ferrous
They consist of dense connective tissue. Such formations are more often formed in women during menopause and can reach large sizes.
-
Fibrous
The organ descends lower, and the cervix becomes visible at the entrance to the vagina. At this stage, discomfort becomes more noticeable. Urination disorders and constipation due to pressure on the intestines appear.
-
Glandular-fibrous
This is a mixed type, including both glandular and fibrous elements.
-
Adenomatous
These are the most dangerous formations, as their cells tend to degenerate into malignant ones. They are necessarily removed, and the woman is under the supervision of a doctor.
Treatment of uterine polyps
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a procedure in which an endometrial polyp is removed using a special instrument equipped with a camera. This not only allows the polyp to be removed, but also allows the inside of the uterine cavity to be examined.
How the procedure is performed:
- The patient is given light anesthesia to avoid discomfort
- A thin hysteroscope with a camera is inserted through the cervix. The doctor examines the uterine cavity to accurately determine the location of the polyp
- The adenoma is removed using a special loop or microscopic scissors
- The removed material is sent for histological examination to determine whether it is benign or requires additional monitoring
Hysteroscopy takes about 20-30 minutes, after which the patient quickly recovers. Usually, you can return to your normal life within a day.
Hormonal therapy
If adenomas are associated with hormonal imbalance, doctors often prescribe hormonal treatment. It helps reduce the risk of new uterine polyps after removal.
What drugs may be prescribed:
- Progesterone tablets or injections. They reduce the effect of estrogens on the endometrium and slow its growth
- Hormonal intrauterine device. For example, the levonorgestrel device (Mirena) releases hormones locally, without affecting the entire body, and helps prevent relapses
- Combined oral contraceptives. They are used if you need to simultaneously normalize your cycle and reduce the likelihood of new uterine polyps
“Combined oral contraceptives help keep endometrial growth under control. They reduce the effect of estrogens, which can provoke tissue growth, and add the right amount of progesterone. This creates a balance in which the endometrium grows evenly, without excess. Thanks to this, new uterine polyps do not form, and the cycle becomes stable and predictable. This approach allows not only to eliminate the problem, but also to prevent its recurrence,” says the gynecologist.
Medicinal support after removal
After removing the adenoma, it is important to help the uterine endometrium recover. Doctors may prescribe:
- Medications that reduce inflammation
- Vitamins and microelements (for example, iron, if there was heavy bleeding)
- Antibiotics, if there is a risk of infection
If neoplasms recur repeatedly, especially during menopause, doctors may suggest removing part of the endometrium (ablation) or even the uterus (hysterectomy). These are extreme measures that are used only if there is a high risk of malignant degeneration.
Is it possible to treat adenomas without surgery? If the polyps of the uterine endometrium are small, do not cause symptoms and do not grow, the doctor may suggest observation. But this is a rare case. Surgery is the most reliable way to get rid of the polyp and prevent complications.
If you are faced with the problem of uterine polyps, do not delay your visit to the doctor. At the K+31 clinic in Moscow, we offer modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of neoplasms so that you can return to normal life without pain and anxiety. We have transparent prices - all of them are on the website. Just call and make an appointment at our center - we will take care of you!
Answers to popular questions
Doctors' answers K+31:
Is it possible to not notice polyps if they do not bother you?
Yes, it is quite possible. Adenomas often do not cause pain or other obvious symptoms, especially if they are small. They can be accidentally found on ultrasound during a routine examination. So even if nothing bothers you, do not forget about regular visits to the gynecologist. Prevention is always easier than treatment.
What influences the risk of developing polyps?
The main factor is hormones. Excessive estrogen levels can stimulate endometrial growth, which increases the likelihood of tumors. Risks also increase with age (after 40 years), in the presence of chronic inflammation, obesity, or multiple curettage. Even stress and an unhealthy lifestyle can play a role.
How can polyps affect your cycle and menstruation?
Adenomas can disrupt the normal functioning of the endometrium, leading to irregular or heavier periods, and sometimes bleeding between cycles. This can be very annoying, especially if the problem becomes chronic. If you notice that your cycle is getting out of order or your periods are becoming painful, this is a reason to see a doctor.
Do all polyps need to be removed?
Not all adenomas require removal. If the polyp is small and does not cause pain or problems, you can simply observe it. But if the uterine polyp interferes, causes bleeding, or there is a risk of degeneration, it must be removed. In any case, the decision is made by the doctor after examination.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
Hormone therapy
Radio wave gynecology with the Surgitron deviceLaser therapy using the Photona device
Sling operations Ectopic pregnancy Delayed menstruation Removal of the uterus (hysterectomy) Thrush (vaginal candidiasis) Prolapse of the uterus and vagina Cervical dysplasia Adenomyosis Treatment of sexual infections Vaginitis (Colpitis) Erythroplakia of the cervix Endometritis Bacterial vaginosis Symphysitis (symphysiopathy) Erosion and ectopia of the cervix Vulvovaginitis Premenopause Uterine artery embolization for uterine fibroids Cervicitis Gynecologist consultation Dysmenorrhea (painful periods) Amenorrhea Removal of the ovaries (oophorectomy) Postmenopausal Sphinctermetry Treatment and intimate rejuvenation with the Fotona laser Adenomyosis (Endometriosis of the uterus) Vulvitis Vaginal surgeries Inflammation of the appendages (adnexitis, salpingo-oophoritis) Labiaplasty (labiaplasty) Bartholinitis Surgery to remove an ovarian cyst Prolapse (prolapse) of the uterus and vagina Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) First menstruation 7 days after embryo transfer Biochemical pregnancy IVF protein diet Day 5 after embryo transfer Follicles Bicornuate uterus and pregnancy Day 9 after embryo transfer 1 day after embryo transfer Age and Fertility 10 days after embryo transfer








































