MRI of the knee joint
MRI of the knee is performed for a detailed examination of the ligaments, muscles, cartilage, meniscus, kneecap, tendons, vessels, nerve endings and bone tissue of the joint. Using magnetic resonance imaging, the doctor obtains clear layered images to visualize damage, inflammation and other pathologies of this area of the musculoskeletal system. A distinction is made between MRI of the knee with and without contrast.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Indications for MRI of the knees
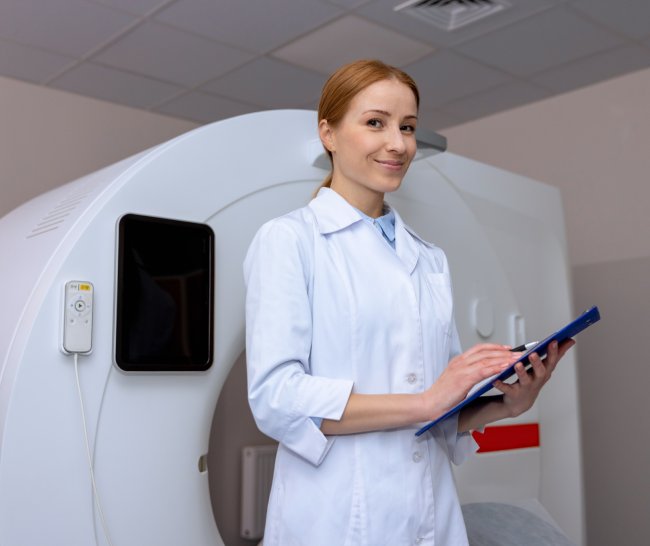
An orthopedic surgeon, surgeon, oncologist, therapist or other specialist refers a patient to have an MRI of the knee joint if:
- The need to clarify the diagnosis after the initial examination using other methods
- Complaints of frequent pain in the knees, swelling, crunching of joints when moving
- Sports injuries
- Diagnosed fluid accumulation
- Decreased mobility or a feeling of instability in the joint
- Suspected ligament or tendon rupture, meniscus damage
- Complications after installation of implants or endoprostheses
- Primary or secondary examination in oncology
- Infectious pathologies (osteomyelitis)
- Examination before surgery - arthroscopy, surgery after injury
Diagnostics is important for diagnosis and adequate treatment. In the images, the doctor will see not only pathologies in tissues, bones or cartilage, but also determine the cause of their occurrence. In oncology, it is possible to determine the stage and extent of tissue damage.
General information about the procedure
Answers to popular questions
How is an MRI of the knee joint performed?
The patient lies down on a table that slowly moves into the tunnel. The limbs are fixed with soft rollers. As the scanner moves, the magnetic field is directed at the object being examined, then, under the effect of resonance, the waves are reflected. The sensor receives the signal and converts it into clear images on the screen. During the entire procedure, you cannot move so that the picture is clear.
When performing an MRI with contrast, a standard series of images is first taken, then a special ferromagnetic fluid (gadolinium) is injected into the patient's blood. This is done by intravenous injection. The scan is then repeated.
The technique involves comparing images before and after the introduction of a contrast agent.
How long does it take to do an MRI of the knee joint?
The diagnostics takes about 30 minutes in standard mode and about 45 minutes when using a contrast enhancer.
What does it feel like during an MRI? While the machine is working, the patient feels warmth and a slight tingling sensation in the knee area, which is normal. The scanning procedure and the injection of contrast agent are painless. If pain or burning occurs, the patient can stop the machine by pressing a button inside the tunnel. A built-in microphone and speaker are provided for communication with the doctor.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
MRI of bone structures
MRI of the spine
MRI of the thoracic spine
MRI of soft tissues of the neck
MRI of soft tissues of the limb
MRI of the pancreas
MRI of the coccygeal region
MRI of the bile ducts and ducts (cholangiography)
MRI of the bladder
MRI of the chest organs
MRI of the head
MRI of the kidneys
MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
MRI of the upper and lower extremities
MRI of the arteries and veins of the brain
MRI of the lumbosacral spine
MRI of the pelvis






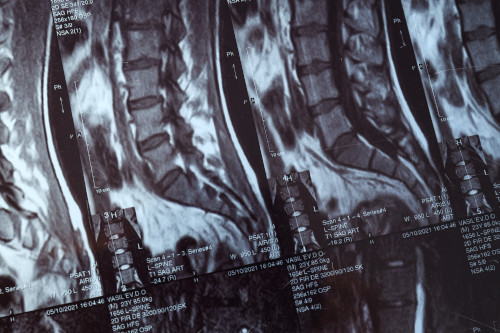





























What does an MRI of the knee joint show?
Magnetic resonance imaging is an effective method for diagnosing knee joint diseases, which is more informative than CT or X-ray. The study is prescribed to confirm the initial diagnosis or to assess the condition after treatment.
What the doctor can see in a series of layered MRI images of the knees:
A standard examination includes layered images of the knee in different projections (in flat and three-dimensional space).
If oncology is suspected, the doctor recommends doing an MRI with contrast enhancement. With this type of diagnostics, a specialist can accurately study the structure of blood vessels, damaged tissues and neoplasms. In the presence of cancerous tumors, it is possible to determine their clear boundaries and sizes, the presence of metastases.