MRI of the temporomandibular joint

specialists

equipment

treatment
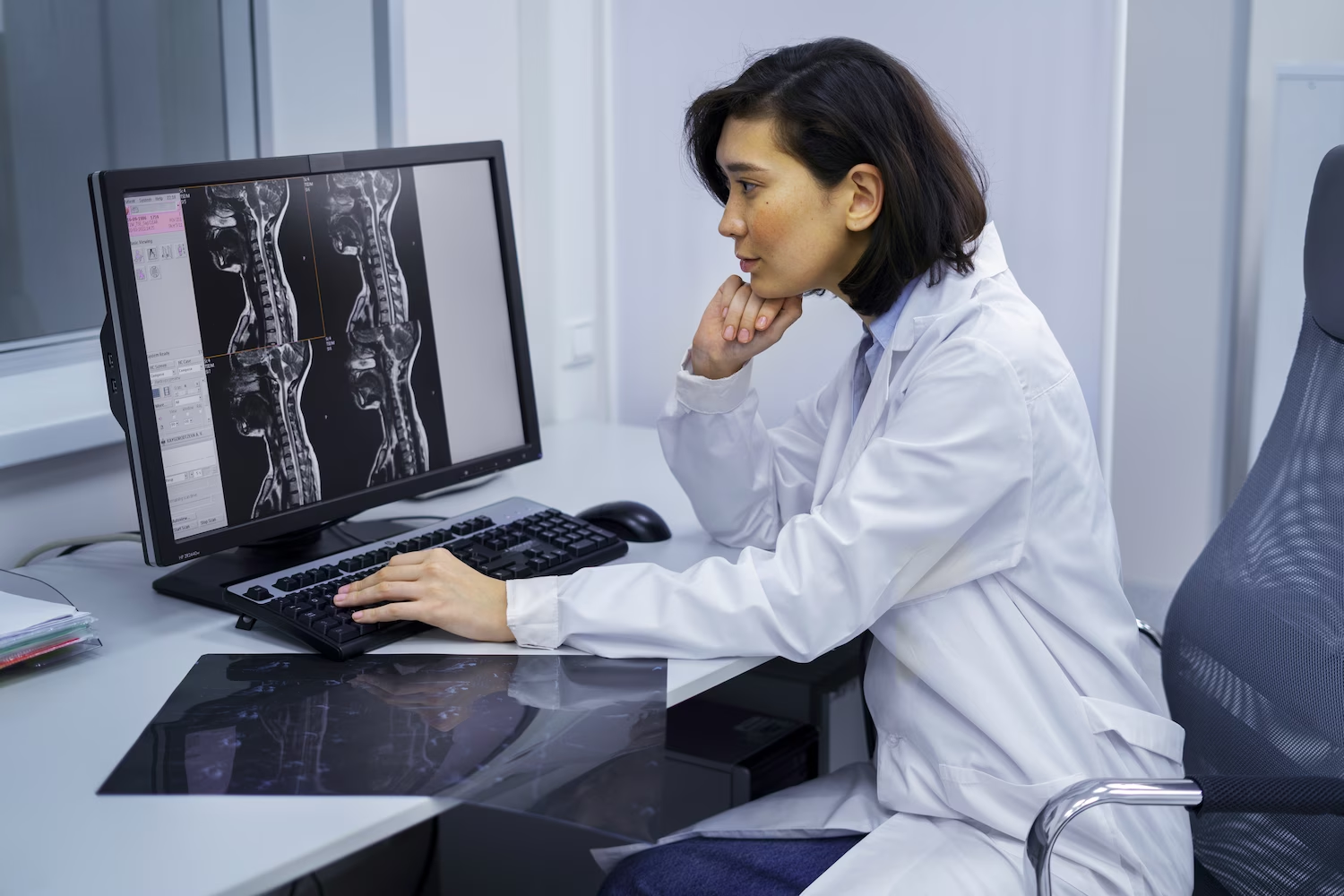
In clinical practice, MRI has undeniable advantages over other diagnostic methods and has a high information value. No other method can detect tumors up to 1 mm in size, and this is an important condition for the success of modern cancer treatment.
Why is MRI of the maxillofacial joint better:
- Diagnostics of neoplasms at the earliest stages
- Accurate image of all structures - bone, cartilage, soft tissues, blood vessels
- It is possible to conduct a dynamic study, when the patient opens and closes his mouth during the session
- No radiation exposure, unlike CT, radiography
- Minimal contraindications; no need to recover after examination
Radiography rarely shows the initial stages of pathological changes in tissues, visualizing solid structures. Ultrasound can help diagnose changes in cartilaginous articular tissue, but MRI provides the most accurate picture of the position of the disc, soft tissue structure.
The leading methods for diagnosing this area are computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, and MRI has significant safety advantages. CT is used as a secondary, additional diagnostic method to clarify the degree of degenerative changes in joint tissues, periarticular zones.
Diagnostics is variable, each option is selected for specific cases, because it provides more information about the area under study.
Types of MRI of the temporal bones, the joint of the lower jaw:
- Native, performed without the use of contrast. Allows you to examine the structures, determine inflammatory, degenerative phenomena in the bone, cartilage
- With contrast enhancement. This study is more informative, as it helps to clearly highlight tumors, starting with a size of less than 1 mm. Contrast allows you to examine the structure of neoplasms, the condition of tissues - both hard and soft at the same time, the degree of involvement in the process
In addition, contrast and native MRI in dentistry, maxillofacial surgery, traumatology, ENT, etc., concerning the joint of the lower jaw, can be carried out with a functional test. To do this, during the examination, the patient is asked to slightly open, open, close the mouth, which allows for joint scans to be taken in different positions. This method serves as the leading method for diagnosing intermittent dislocation, subluxation of the joint, dysfunction of the structure, joint capsule, meniscus defects. Using functional images, the doctor will determine at what point the functionality failure occurs, this will reveal non-obvious causes of jaw dysfunction or pain.
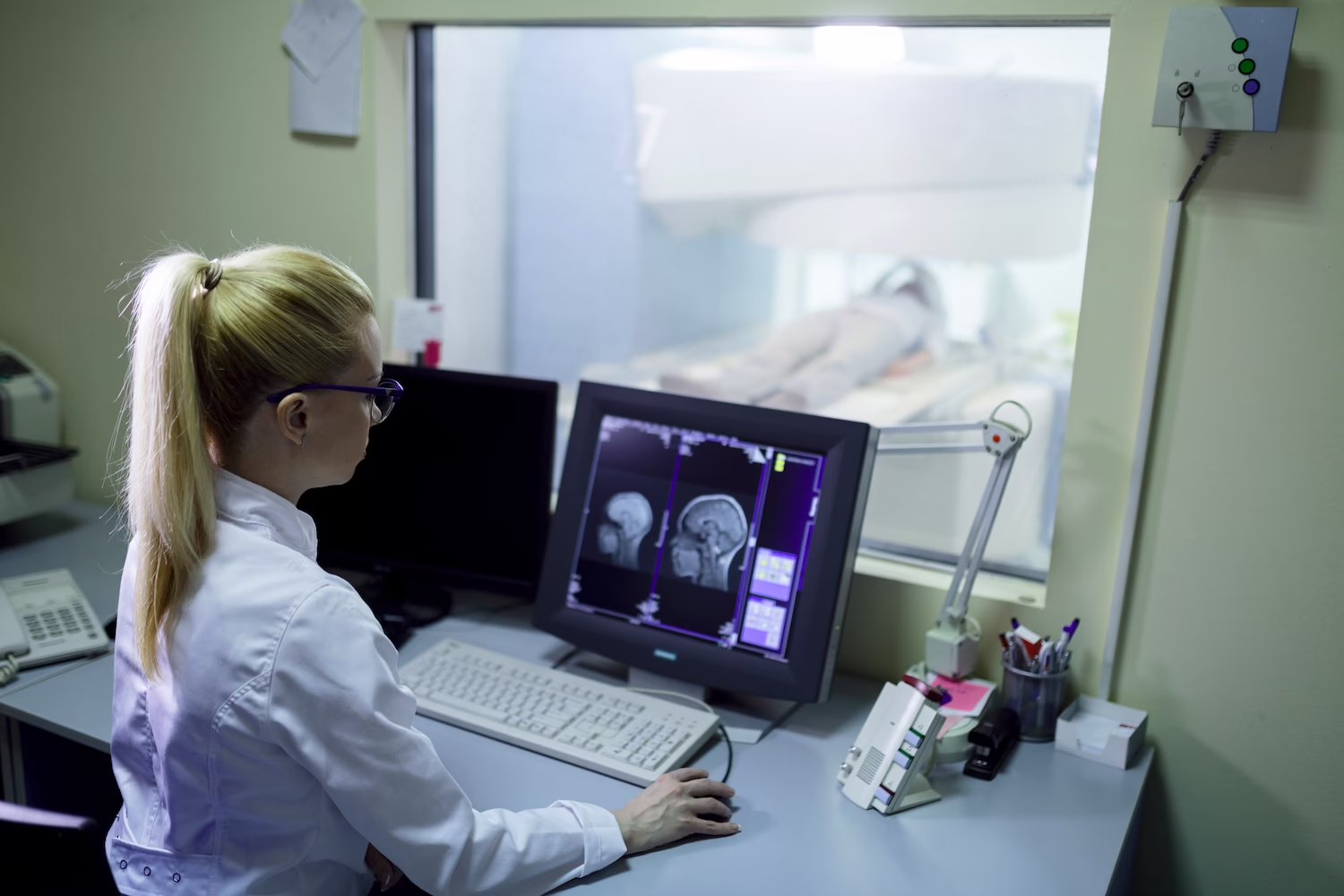
Like any other joint, the temporomandibular joint can be subject to inflammatory, rheumatic pathologies. It experiences a large daily load during chewing, so any violations of its anatomy or functionality affect the person's condition. In severe, advanced cases, pathologies can become temporary or permanent obstacles to chewing solid, semi-solid food, this will entail other disorders of the digestive tract, endocrine system, and other structures of the body.
Indications for TMJ MRI:
- Pain in the area of the temporomandibular joint during chewing movements, talking, yawning, at rest. Painful sensations can radiate to the back of the head, ears, temple, face, lateral surface of the neck, under the cheekbones. Pain may be unilateral or bilateral
- Swelling, redness of one or both joints of the lower jaw
- Constant crunching, clicking, sensation of subluxation of the joint
- Habitual dislocation of the lower jaw, several episodes in the anamnesis
- Nodular formations under the jaw or in the joint area
- Limited movement in the joint, inability to open or close the mouth wide, eat
- Numbness of the face
- Spastic phenomena when eating
- Enlarged lymph nodes on the neck, in the ear area, on the back of the head
- History of injuries
- Nervous tic of the facial muscles
- Bite anomalies
The doctor will prescribe an examination before the planned installation of dentures, dental prosthetics, installation of braces, bite correction procedures, plastic surgery.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
MRI of bone structures
MRI of the spine
MRI of the thoracic spine
MRI of soft tissues of the neck
MRI of soft tissues of the limb
MRI of the pancreas
MRI of the coccygeal region
MRI of the bile ducts and ducts (cholangiography)
MRI of the bladder
MRI of the chest organs
MRI of the head
MRI of the kidneys
MRI of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space
MRI of the upper and lower extremities
MRI of the arteries and veins of the brain
MRI of the lumbosacral spine
MRI of the pelvis






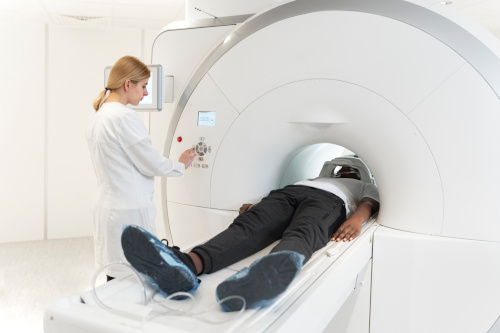































What is MRI of the TMJ, the essence of diagnostics
The technique is based on the phenomenon of nuclear magnetic resonance. Hydrogen atoms in the cells of living tissues react to radio frequency pulses in an electromagnetic field, and each type of cell has its own characteristic response. This picture is processed by a computer in the form of slice images, which allow you to study the state of the studied area layer by layer. The 3D format is convenient for examining the structure from different sides, which is impossible in other diagnostic techniques.
MRI of the jaw, joints provides complete information about the state of all structures, tissues, pathological foci and changes, functionality, histological features of the altered tissue.
Thus, it is possible to diagnose benign and malignant neoplasms, injuries, damage to the articular meniscus, arthritis, arthrosis, vascular dysfunction, congenital deformities.