MRI of the cervical spine

specialists

equipment

treatment
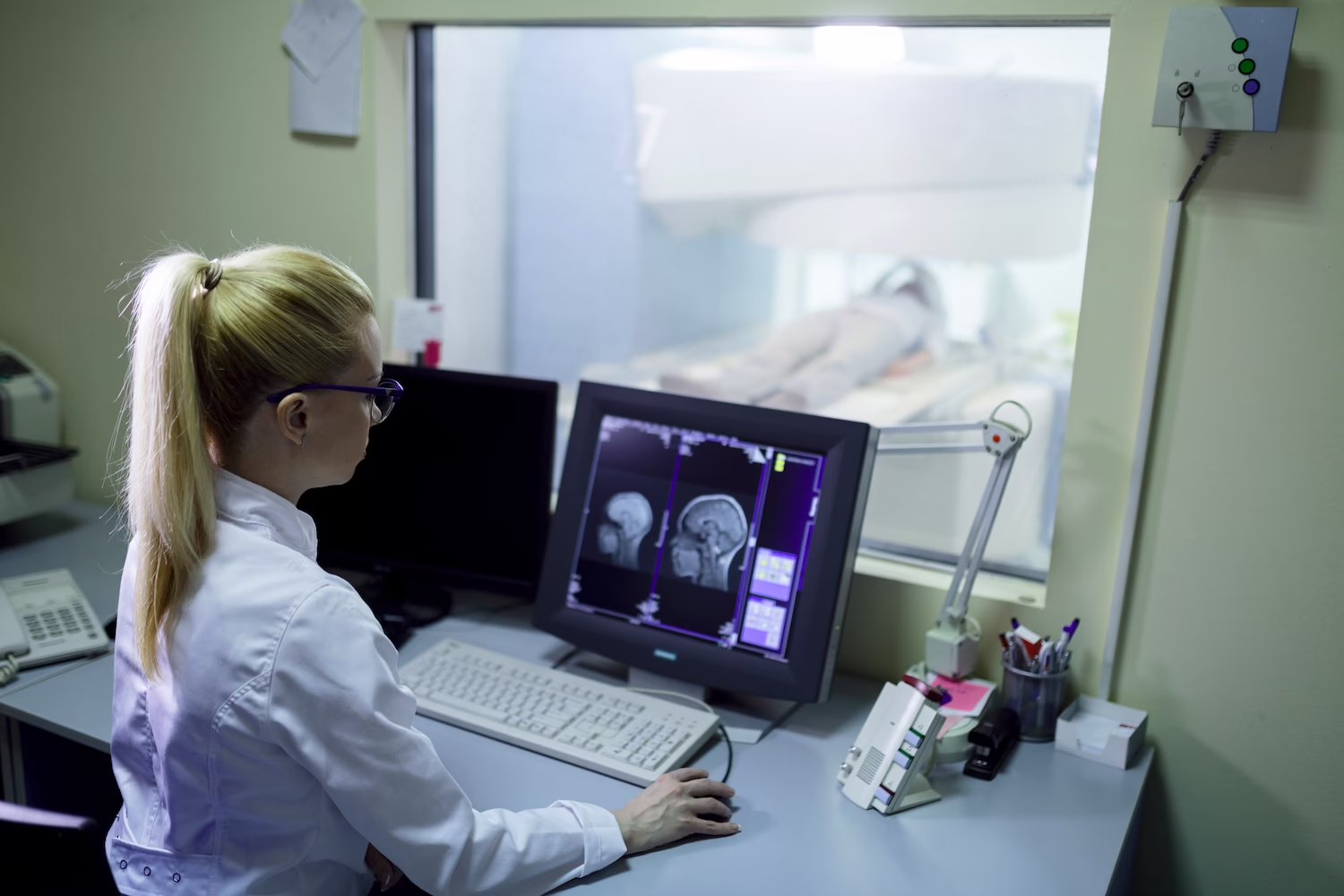
An orthopedist, traumatologist or surgeon may refer a person for diagnostics for the following diseases and symptoms:
- Dizziness
- Intervertebral hernias
- Radiculitis
- Suspected spinal stenosis
- Pain in the head, cervical-collar zone and/or upper limbs
- If a feeling of stiffness appears in the cervical-collar zone
- Suspected neoplasms with metastases in the vertebrae and spinal cord in the cervical region
- To confirm the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis or control during therapy
- As part of postoperative monitoring of the condition of the cervical spine column
- For diagnostics of abnormal developments of the spine
- For inflammatory processes in the spinal cord
Doctors recommend undergoing MRI diagnostics annually to prevent possible problems and pathologies of the spinal spine.
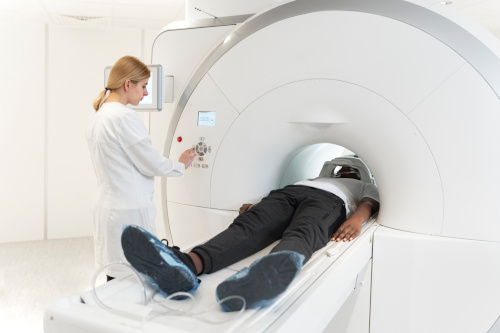
The method is absolutely safe. It can be performed on children and elderly people. During the procedure, the body is not exposed to X-rays, radiation or other types of radiation. However, since the human body is in the area of magnetic radiation during diagnostics, there are a number of limitations to diagnostics:
- MRI of the cervical spine is not performed if there are metal structures and elements in the body: prostheses, pacemakers, insulin pumps, vascular clips, etc. The exception is titanium prostheses
- Patients with claustrophobia are recommended to undergo the procedure in open-loop devices or in a state of drug-induced sleep
- MRI of the cervical spine with contrast is not performed during pregnancy and lactation, as well as in cases of renal failure or intolerance to the contrast agent
Before the examination, it is important to warn the diagnostician about all regularly taken medications and existing implants. This is necessary so that the procedure does not have negative consequences for health.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services










































MRI of the SHOP: what is it?
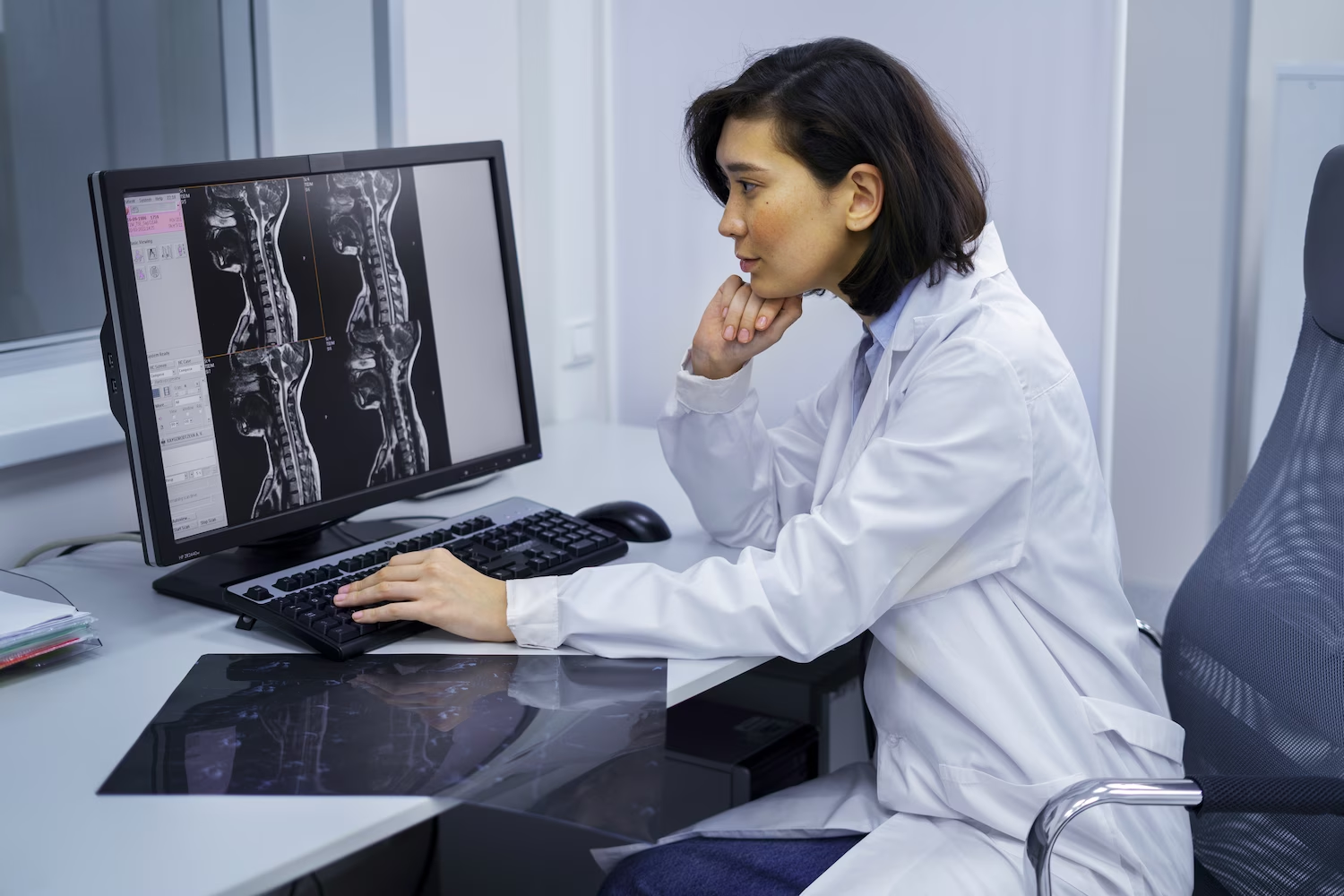
With the help of magnetic resonance imaging, a doctor can detect not only bone diseases, spinal disorders or spinal cord pathologies. This technique also provides access to information about the soft tissues near the spine and their condition.
What will an MRI of the cervical spine show? The study makes it possible to detect:
This diagnostic method is currently recognized as the most accurate and informative. Taking into account what the MRI of the cervical spine shows, the doctor can assess the size and configuration of nerve endings, blood vessels, ligaments and muscles of the spinal column. In most cases, tomography is the only way to determine the type and location of the disease, assess the condition of the spinal cord tissues and make an accurate diagnosis.