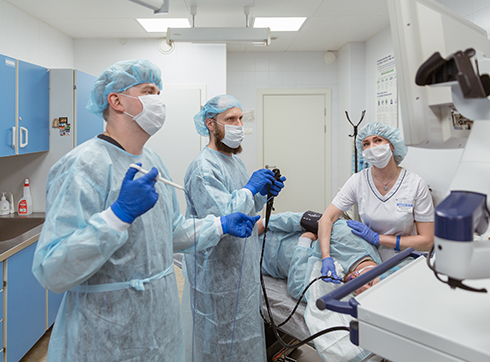
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) - the casting of duodenal and / or gastric contents into the esophagus, which leads to damage to the distal section as a result of inflammatory lesions of the mucous membrane - reflux esophagitis (RE) and the appearance of erosive-ulcerative changes in it.
Reflux esophagitis - damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, which is visible during gastroscopy (endoscopy). It is observed in approximately 30-45% of patients.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease without esophagitis (otherwise endoscopically negative reflux disease, or non-erosive reflux disease) - damage to the mucous membrane of the esophagus, which is not diagnosed by endoscopic examination. The disease is detected in more than half of patients.
Factors contributing to the development of GERD
- HHAP (hiatal hernia);
- smoking;
- increased intra-abdominal pressure (overweight, pregnancy) and others.