Treatment of stomatitis

specialists

equipment

treatment
How does the disease manifest itself?

Symptoms of stomatitis can vary significantly depending on its form and stage of development. The onset of the disease is often characterized by redness of a certain area of the oral mucosa. Such a spot usually does not protrude above the surface of the mucous membrane, has a round or oval shape, pink or white color. Gradually, swelling forms around the affected area, which is accompanied by pain.
Later, at the site of the original spot, an aphtha (ulcer) is formed - a superficial defect of the mucous membrane, which has a round shape and is covered with a grayish fibrinous coating. Aphthae are usually localized in the following areas:
- Transition fold
- Lateral surface of the tongue
- Mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips
When removing necrotic plaque from the aphthae, bleeding may begin.

In more severe cases, the amount of fibrinous plaque on the surface of the ulcers increases. An infiltrate appears at the base of the ulcer, which consists of cellular elements of blood and lymph. This leads to the following signs of stomatitis:
- Pain
- Burning and itching
- Bad breath
- Increased saliva production
Eating becomes difficult, and the general condition worsens. The patient may complain of increased body temperature and general weakness.
In the most severe cases, multiple deep ulcers occur on the mucous membrane, which cause significant discomfort. Such ulcers are surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate and have jagged edges. They often lead to inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes, their increase in size and pain on palpation.
Classification of stomatitis
According to the type of lesion
The World Health Organization (WHO) divides stomatitis into several main types, each of which has its own characteristics and potential risks. What do different types of stomatitis look like in the mouth:
- Catarrhal stomatitis is the most common type, in which swelling and redness of the mucous membranes are observed. A yellowish-white coating often occurs, which causes discomfort in the mouth
- Aphthous stomatitis - characterized by the formation of blisters that burst and turn into grayish ulcers with red edges. This type is considered more painful and causes significant discomfort when eating and talking
- Ulcerative stomatitis – plaque is present, which may cause bleeding when removed
Advanced forms of ulcerative stomatitis can lead to otitis media, pleurisy, and endocarditis.
Based on causes
In addition to classification by type of lesion, stomatitis is divided into 5 types according to the reasons for its occurrence:
- Bacterial - often develops against the background of other diseases caused by bacterial infections, for example, sore throat or sinusitis
- Herpetic - occurs in carriers of the herpes virus when the immune system is weakened
- Candida – develops as a result of activation of fungi of the genus Candida, usually against the background of decreased immunity
- Allergic – most often appears after contact with pollen or mold spores. Fillings and prosthetic crowns made from low-quality materials also contribute to the development of the disease
- Mechanical - occurs as a result of mechanical damage to the mucous membrane
If the disease occurs regularly, it can become chronic. Advanced stomatitis is accompanied by bad breath and increased body temperature. It is painful for the patient to eat, drink and talk, a lot of saliva is produced, and a tingling sensation in the mouth bothers him.
General information about the procedure

Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment at "K+31"
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
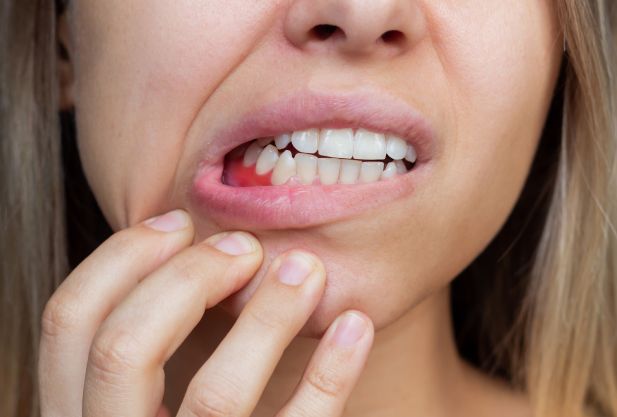


























































Why does stomatitis appear?
Stomatitis is not considered a contagious disease. The exception is herpetic stomatitis, which is transmitted by airborne droplets and contact.
In most cases, stomatitis occurs due to exposure to external and internal irritants that activate the immune system. Let's look at the main causes of stomatitis.
Viral and bacterial infections are common causes of stomatitis in children. They enter the oral cavity from unwashed hands or dirty toys. The disease can also be caused by minor injuries, such as biting the cheek or scratching after eating hard foods.
In adults, the development of stomatitis can be triggered by chronic diseases, acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI), helminthic infestations, and HIV infection.