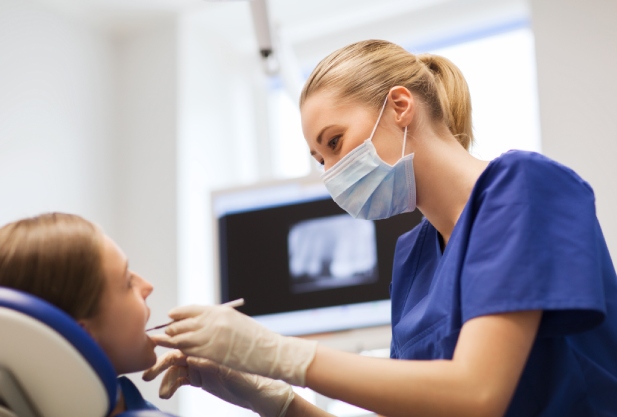
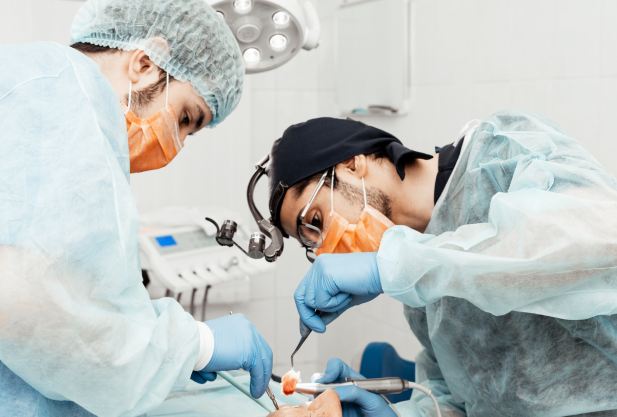
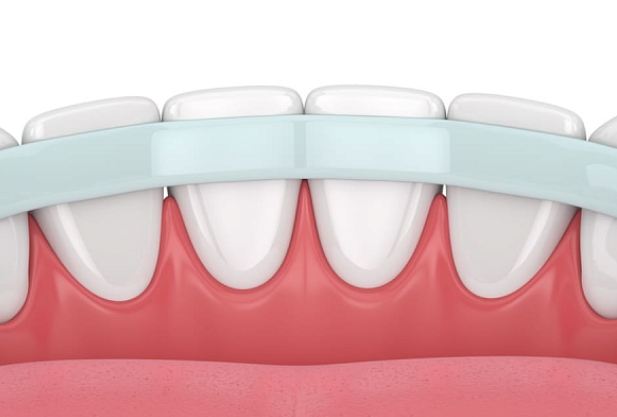
Treatment of periodontal disease

specialists

equipment

treatment
Stages of development of periodontal disease
Periodontal disease progresses over several years.
Damage to periodontal tissue can be both acute and chronic. In addition, depending on the area of damage, there are 2 types of the disease.
The localized type is manifested by exposure of the dental necks in a specific area. The generalized type is characterized by pathological changes covering the entire dentition.
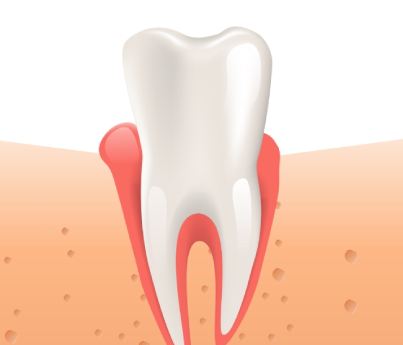
During the diagnostic process, the following stages of pathology are detected:
- Initial It often goes unnoticed, as there is almost no pain. Some patients notice slight gum bleeding when brushing their teeth. Also, in the early form of periodontal disease, slight swelling and redness of the gums is observed. Inflammation does not yet affect deep tissues, and teeth do not become loose
- Moderate Increased bleeding of the gums even with a light touch (for example, when eating hard foods), sensitivity of the gums, change in their color to a darker one. Inflammation progresses, periodontal pockets begin to form, in which food debris and microbes accumulate
- Heavy Significant retreat of the gums from the teeth, exposure of the roots of the chewing units. The teeth begin to loosen and change their position in the row. The bone tissue of the jaw is gradually destroyed
Answers to popular questions
Doctors at K+31 (Moscow) answered the most common questions about this pathology.
Can I get braces if I have periodontal disease at the age of 45 or older?
Is it painful to treat periodontal disease?
Is treatment possible with traditional medicine?
How long does treatment take?
How to prevent the development of periodontal disease?

Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment at "K+31"

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price

Callback request
Services
Orthopedic dentistry
Orthodontics Treatment of periodontitis Children's dentistry 3D scanning Children's dental treatment Сaries treatment Consultation of a dentist orthopedic prosthetist