Treatment of dental cyst

specialists

equipment

treatment
Classification
Doctors classify dental cysts according to two main characteristics: location and causes of formation.
Depending on location
The main types of cysts by location include:
- Wisdom tooth cysts that occur in the area of the third molars
- Formations caused by improper installation of dental crowns. They lead to improper distribution of the chewing load and the development of inflammatory processes
- Cysts that form under the influence of infectious diseases, such as pharyngitis
- Formations that are localized in the area of the front teeth. They are often associated with injuries or caries
In rare cases, patients are diagnosed with a calcifying cyst. With this diagnosis, the formation is filled with turbid liquid and is clearly visible on x-rays. A cyst can form anywhere in the jaw, but most often it is found in the lower part. Treatment requires resection.
Depending on the causes
Depending on the causes of cysts, there are:
- Residual. Occur after poor-quality removal of one or more teeth, where residual tissue becomes a source of infection
- Eruption cysts. Develops in children during the eruption of milk or molar teeth
- Retromolar or paradental formations. Caused by the growth of wisdom teeth
- Radicular cysts. Considered a complication of periodontitis
- Primordial or keratocysts. Occur due to degeneration of the tooth-forming tissue
Each type of cyst has its own characteristics and requires an individual approach to treatment. For example, radicular cysts often require surgery. Formations caused by inflammatory processes in the gums are eliminated during treatment of the underlying disease.
Cyst symptoms

The departure of the gum from the tooth and exposure of its root manifests itself clinically in a variety of ways. Each of these symptoms may indicate certain diseases in the oral cavity.
One of the common signs of recession is bleeding and swelling of the gums, as well as changes in their color. This may be an indicator of periodontitis.
Another manifestation is the peeling of the gum from the tooth, the formation of pockets. This may indicate an advanced stage of periodontitis, often accompanied by purulent formations and bad breath, which increases the risk of tooth loss.
Pale or whitish gums may be a symptom of periodontitis, which is characterized by impaired blood microcirculation and leads to thinning and weakening of the gums.
Increased sensitivity, especially to temperature or sweets, is a consequence of exposed roots. This increases the risk of developing caries in these areas.
If teeth become loose, this may indicate serious damage to periodontal tissues.
Localized gum recession affecting one or two teeth often occurs due to mechanical trauma, such as improper use of toothpicks.
Why is a dental cyst dangerous?

Although a cyst over a tooth seems harmless, it can lead to serious complications. Among them:
- Suppuration and inflammation of cystic tissues, causing an infectious process
- Spread of inflammation to the lymph nodes, which worsens overall health
- Damage or destruction of bone tissue in the area of the diseased tooth, which affects the stability of the dentition and jaw as a whole
The chronic process can spread to the maxillary sinuses and cause sinusitis. It also threatens the development of lymphadenitis, osteomyelitis, and periostitis.
If the protective capsule of the cyst bursts, this creates favorable conditions for the spread of pathogenic microorganisms to neighboring tissues. The source of inflammation increases, which worsens the patient’s well-being.
In addition, you must be aware that if left untreated, the affected area of bone may become more fragile. This increases the risk of spontaneous jaw fracture.
General information about dental cysts
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other Services



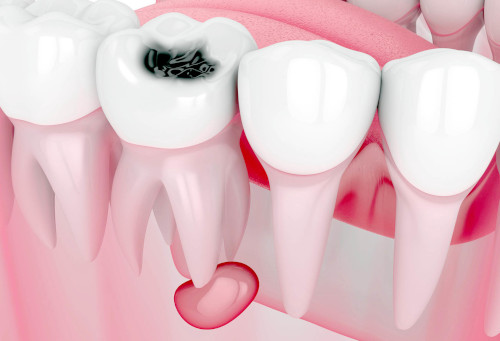





















































Causes of dental cysts
One of the common causes of cyst development is deep caries. Gradually, it has a negative effect on the dentin structure, leading to an infectious process and inflammation of the pulp. This threatens the formation of a granuloma, which is subsequently filled with a mixture of pus and ichor.
In addition, a dental cyst occurs due to the following reasons:
To prevent complications, it is important to consult a doctor, undergo an examination and follow all recommendations.