Fissure sealing to protect teeth from caries

specialists

equipment

treatment
Fissure sealing techniques in dentistry

There are two main approaches to fissure sealing: non-invasive and invasive.
Non-invasive sealing does not require prior intervention in the structure. Here a sealant is used to fill the recesses. The procedure does not cause pain, which makes it suitable for a child’s first introduction to dental treatment. However, there is a risk of enclosing the initial stages of caries under the sealant. If the disease has already penetrated into deeper layers, sealing can provoke its further development under the protective layer.
The invasive technique involves removing the top layer of enamel to better fix the sealant. This approach ensures deep cleansing of fissures and increases the effectiveness of the procedure. However, it does come with certain risks: if the sealant is lost, the treated areas become more vulnerable to tooth decay and may cause increased sensitivity. This method requires specialized equipment and materials, which affects the cost of the procedure.
Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages; the choice depends on the specific situation and condition of the patient’s teeth. It is important that the decision on the sealing method is made by the doctor, taking into account all factors.
Fissure assessment
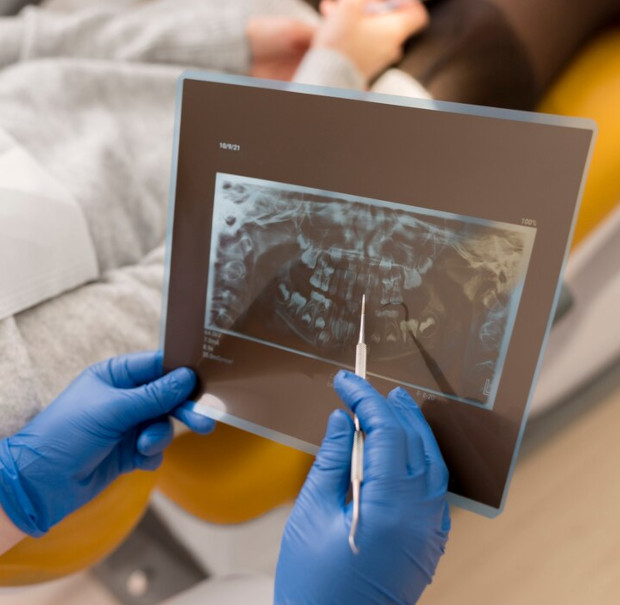
To detect the initial stages of caries in the grooves, a number of methods are used, important for preventing further tissue destruction. Visual examination is the primary and accessible diagnostic method, but its effectiveness is limited - about 25%. This is due to the fact that the instrument may not reach all the grooves, and the procedure may be unpleasant for people with sensitive teeth.
For more accurate detection of caries, the following methods are used:
- Radiography allows you to see hidden damage that is not visible to the naked eye
- Fissurotomy is necessary to expose and assess the depth of carious lesions in hard-to-reach places
- Electrometry assesses the degree of tissue mineralization, which helps to identify caries in the early stages
- The laser fluorescence method is considered one of the most effective today, as it allows you to determine the presence of caries at any stage of its development
These methods complement each other, allowing the doctor to obtain the most complete picture of the condition of the fissures and, on this basis, make an informed decision about the need to seal them. It is important to remember that only an integrated approach to diagnosis can prevent the progression of caries.
Advantages and disadvantages of fissure sealing in children
Sealing cracks in children has its pros and cons.
But sealing the tooth fissure with sealant also has disadvantages. If existing tooth decay is not noticed during the procedure, it can cause problems. Improper application of sealant can affect your bite. In adults, there are deep and stained fissures, which makes the procedure difficult to achieve. Sealing is not a substitute for regular cleanings and dental visits. Careful control, especially of the bite, is important to avoid malocclusion.
Among the advantages:
- Prevents Cavities Sealants create a protective layer that reduces the risk of tooth decay, especially on teeth that we use to chew
- Better hygiene Sealed cracks are easier to clean, reducing the buildup of bacteria and food debris
- Durability The procedure helps preserve teeth, avoiding complex and expensive treatment in the future
- Help during orthodontic treatment Sealing provides additional protection against caries during bite correction
Protection of teeth grooves in children
The process of caring for children's smiles begins with baby teeth, often between the ages of two and three. This is the period when their complete release from the gums allows for a seal that reduces the likelihood of developing caries for many years, subject to proper oral care. The risk of developing caries can be reduced by up to 90%.
After analyzing the data obtained, the doctor determines the treatment approach: conservative or surgical. In case of removal, an important step is rehabilitation to prevent complications and speed up recovery.
The benefits of fissure sealing in permanent teeth in children become obvious when the child reaches the age of five and his first permanent molars begin to emerge. During this period, oral hygiene becomes more difficult due to the depressions where food debris can accumulate, contributing to the formation of caries. To maintain the health of these teeth, the following approach is recommended:
- Regular plaque removal
- Ensuring proper cleaning
- Timely sealing of grooves
When a child reaches the age of seven to five years, the first permanent teeth appear in the oral cavity, which are especially vulnerable to caries. This is due to the fact that the enamel has not yet reached its final maturity and mineralization, which occurs in the next three years after eruption. Sealing during this period promotes the formation of strong enamel and prevents food particles from entering the grooves, which is a key factor in preventing tooth decay.
Choosing a sealant for children's teeth
In pediatric dentistry, special sealants are used to protect against caries. These products have a high fluidity, which allows them to penetrate into narrow grooves and recesses. An important advantage is the content of useful microelements in the composition of sealants, such as calcium, fluorine and phosphorus, which help strengthen the enamel.
Depending on their properties, sealants for children can be:
- Transparent, which makes it easier to monitor the condition of the fissures after they are sealed. However, due to its invisibility on the tooth surface, it can be difficult to assess the integrity and wear of the coating
- Opaque, usually milky white, easier to see and monitor
Before the procedure, the dentist discusses the choice of material with the parents. The doctor explains what sealant will be used, its composition and features. Modern specialists in the field of pediatric dentistry value openness in communication and are ready to talk in detail about the upcoming procedure, answering all questions and relieving parents’ concerns.

Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment at "K+31"
Measures to protect baby teeth from caries

To maintain the health of children’s primary teeth, in addition to fissure sealing, it is necessary to follow a number of important rules:
- Balanced diet Including solid vegetables, fruits, dairy and fermented milk products in the diet, as well as limiting the consumption of sweets
- Regular oral care Brushing should be done twice a day, and if using braces, after every meal
- Frequent visits to the dentist It is recommended to visit your doctor every six months, sometimes even more often
- Selection of brushes and toothpastes appropriate for the child’s age It is important to follow your dentist's advice when purchasing dental care products
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other Services
Online consultation with a pediatric dentist
Oral hygiene according to the Swiss GBT protocol Plastic frenulum of the tongue Treatment of baby teeth Dental treatment in a dream





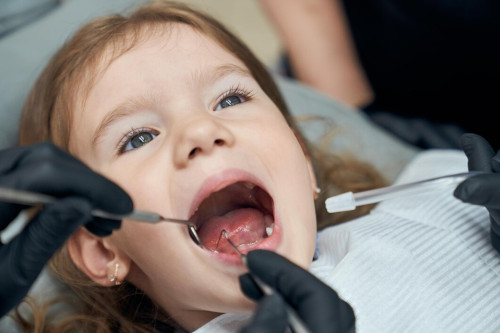















































Who needs sealing and for whom it is not recommended
Sealantization is a procedure that helps prevent tooth decay. It is especially important in the following cases when teeth:
When permanent teeth first emerge, their enamel has not yet fully strengthened, making them more vulnerable to tooth decay. Over time, as mineralization increases, the enamel becomes more protected. For children and teenagers whose teeth are still developing, sealants are an effective way to prevent tooth decay.
However, there are cases when the fissure sealing technique is not recommended:
In these cases, either the natural protective mechanisms of the teeth are quite effective, or sealing will not help, and may even hide the problem, complicating diagnosis and treatment. In such situations, dentists choose other methods of treatment and prevention.