Tympanometry

specialists

equipment

treatment

When is tympanometry prescribed?
- Difficulty in perceiving sounds when the cause is not clear, especially in children
- Deterioration of hearing after illness
- Hearing problems resulting from head injury
- Recurrent ear infections
- Regular colds or sinus infections. Infections easily spread from the nasopharynx to the ear through the Eustachian tube, causing otitis media
- Suspicions of the presence of polyps or other formations in the ear
- Inflammation of the adenoids
- This method is often used in addition to audiometry to clarify the diagnosis, since by itself it cannot determine the degree of hearing loss
Tympanometry procedure: what you need to know
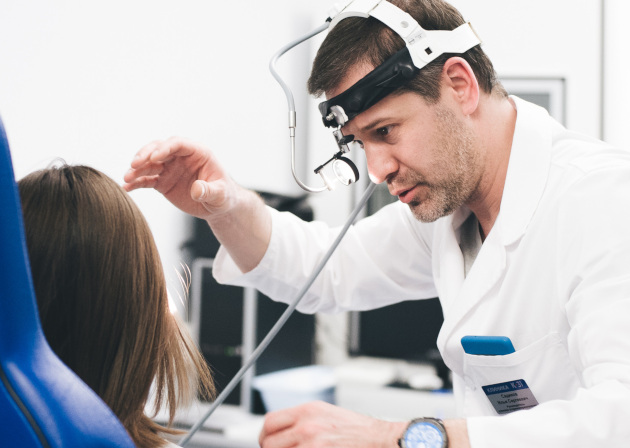
Tympanometry is a painless way to assess the functions of the middle ear, which does not require special training and is suitable for all age groups.
Before the procedure, you need to make sure that there are no:
- Sulfur plugs
- Acute infection
- Fevers
- Violations of the integrity of the eardrum
And also fresh injuries or bleeding in the ear cavity.
Diagnostics takes place on an outpatient basis and is distinguished by its accessibility. It is important that it does not cause pain or severe discomfort, although some patients may experience discomfort due to brief loud noises during the examination. However, the procedure only lasts a few minutes, making it easy to tolerate even for the most sensitive people.
Diseases detected by tympanometry

This procedure helps diagnose various conditions that affect hearing. Here are some diseases that can be recognized using tympanometry:
- Tympanometry for adenoids can detect impaired ventilation in the Eustachian tubes caused by enlarged adenoids. This condition often leads to hearing loss due to fluid accumulation in the middle ear
- Tympanometry for otitis media is used to confirm the presence of fluid behind the eardrum. This method is especially important for diagnosis in children
- Tympanometry for sensorineural hearing loss helps to exclude the presence of organic problems in the middle ear
- Tympanometry for tubo-otitis makes it possible to assess the function of the Eustachian tube and identify its blockage or dysfunction
- Tympanometry for perforation of the eardrum allows you to determine disturbances in acoustic impedance measurements caused by the presence of holes in the eardrum
Where is tympanometry done? This procedure can be performed in many medical institutions, including hospital ENT departments and specialized clinics. Tympanometry according to compulsory medical insurance is also available in public medical centers.
General information about the procedure
Interpretation of tympanometry results
Tympanometry presents the results in the form of diagrams, where the main markers are the vertices. The presence or absence of these peaks, their number and size make it possible to assess the health of the middle ear. There are six basic types of diagrams:
Type A:One central peak symbolizes the normal functioning of the ear. This means that the eardrum and auditory ossicles are working properly, and the pressure in the cavity is normal
Type B:No peaks on the graph may indicate problems including scarring on the eardrum, fluid in the ear, or tumors
Type C:A peak located in an area of low pressure may indicate partial or complete blockage of the eustachian tube
Type D: The presence of two peaks is a sign of excessive mobility of the eardrum, possibly due to thinning or damage
Type E:Multiple peaks or one peak with a peak split into two parts may indicate a disturbance in the sound transmission system, possibly due to damage to the auditory ossicles or inflammation
Type Ad: An excessively high peak, beyond the normal values, indicates increased mobility of the eardrum when probing at low frequencies
Such data requires professional interpretation. An attempt at decryption on your own may be incorrect. The doctor takes into account not only the type of chart, but also general symptoms, as well as the results of other tests.
Consultation with a specialist before tympanometry
Tympanometry is a detailed examination of the ear, prescribed and analyzed by an otolaryngologist. This specialist not only conducts the examination, but also interprets its results, makes a diagnosis and develops a treatment plan. In addition to the ENT doctor, other medical specialists may also resort to the procedure, depending on the situation:
- Audiologists deal with hearing problems and may prescribe tympanometry if there are complaints of hearing loss
- Hear-prosthetists use the research results to accurately select hearing aids
- Otolaryngologist oncologists use tympanometry to diagnose ear tumors
- Oral and maxillofacial surgeons can use tympanometry data in preparation for facial or maxillary surgery, including rhinoplasty
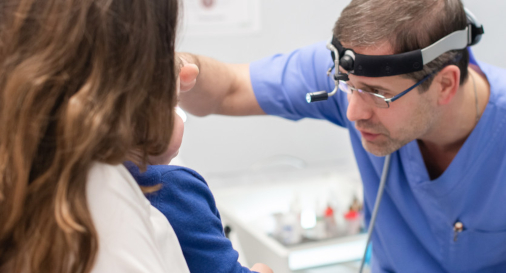
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
































About the service
Tympanometry, also referred to as impedancemetry, is a technique that helps identify diseases of the middle ear and eardrum. The principle of the procedure is based on creating specific pressure in the ear canal and studying the reaction of the eardrum to audio waves.
This diagnostic approach is aimed at identifying disturbances in the transmission of sounds through the bony structures of the middle ear. In a healthy state, the eardrum along with three bones (hammer, incus and stirrup) transmit vibrations to the inner ear. There is an organ of Corti with hair cells that turns these vibrations into nerve impulses that the brain interprets as sounds.
Dangerous anomalies include:
New growths or changes in the function of the eustachian tube can also lead to hearing loss.
To identify such disorders, doctors can prescribe tympanometry in combination with audiometry, which allows them to accurately assess the level of hearing loss and choose the most appropriate treatment method.