Treatment of perforation of the nasal septum

specialists

equipment

treatment
Diagnosis of perforation of the nasal septum
First, the otolaryngologist performs an endoscopic examination. This method allows not only to confirm the presence of perforation, but also to estimate its size.
In addition, in order to exclude autoimmune diseases and the presence of neoplasms, a biopsy is performed. In this case, the specialist takes a sample of the patient’s mucous membrane.

- Blood tests They help identify possible systemic causes of perforation.
- Smear for pathogenic flora It is carried out to determine the pathogen.
- Computed tomography (or ultrasound) This procedure allows you to assess the condition of the paranasal sinuses.
Features of therapy

For small perforations, conservative therapy is carried out. It involves cleansing the nasal passages with antiseptic solutions. If an infection is detected, the patient is prescribed antibacterial therapy. Additionally (if necessary), correction of concomitant diseases is carried out.
If medium-sized perforations (2.5-3.5 cm) are detected, surgery is prescribed. In the process, the specialist cuts out a flap with a vascular pedicle from the patient’s nasal mucosa. The tissue is moved to the defect area and sutured - thereby the doctor closes the resulting hole. The place from which the flap was taken is restored with new mucosa over time.
Rehabilitation after surgery generally takes 1-2 weeks. During this time, it is prohibited to blow your nose and use vasoconstrictors. If pain occurs, it is permissible to use analgesics prescribed by a doctor.
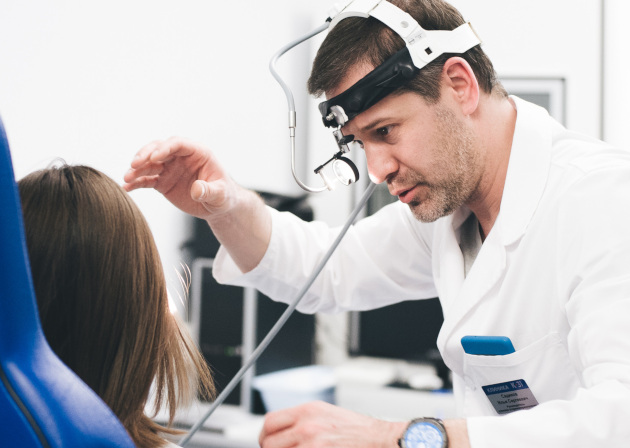
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Reviews 7




























Causes and symptoms of perforation of the nasal septum
In 90% of cases, perforation develops after septoplasty. This condition also occurs against the background of nasal injuries and uncontrolled use of vasoconstrictors. In addition, people who use local drugs (for example, cocaine) are at risk.
The main sign indicating perforation is difficulty in nasal breathing, accompanied by a characteristic whistle.
As the defect increases, mucus or blood mixed with pus is released from the nose. The skin on the front of the nose and tip becomes red and swollen. Additionally, symptoms of intoxication often occur: the temperature rises to 38.5 °C. General weakness is combined with a painful headache.