Treatment of sore throat in children
Sore throat in children (acute tonsillitis) is an infectious-allergic pathology. This contagious disease is characterized inflammation of the tonsils. In the absence of timely treatment against the background of tonsillitis, they appear as early, and long-term complications.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Forms of sore throat
There are several forms of the disease. Most often, catarrhal tonsillitis is detected in children. Less common are follicular, lacunar and gangrenous forms of tonsillitis.
Catarrhal sore throat
This is the mildest form of sore throat, which most often occurs in children. It is characterized by the absence of pus. At the same time, against the background of loose and desquamated epithelium, a thin serous film of a whitish hue appears.
Main symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis:
- Redness and slight swelling of the tonsils
- Mild pain (occurs the day after the redness appears) when swallowing
- General malaise and weakness
In the absence of complications, catarrhal tonsillitis usually lasts from 3 to 5 days. After this, the child gradually recovers.
Follicular tonsillitis
This is a more serious form of sore throat. It is characterized by the presence of purulent pinpoint follicles visible through the epithelial cover of the tonsils. Their size is 2-3 mm. With the development of this form, the pain in the throat often becomes intense.
When swallowing, it intensifies. Additional manifestations of pathology include high temperature (up to 38 degrees), as well as enlarged and painful cervical lymph nodes.
Lacunar tonsillitis
This form is characterized by the appearance of a linear purulent plaque of a yellowish color. It is formed in the lacunae between the lobes of the tonsils.
The main manifestation of the pathology is severe pain in the throat and when swallowing. It is accompanied by high fever and chills. The cervical lymph nodes become greatly enlarged and become painful to the touch.
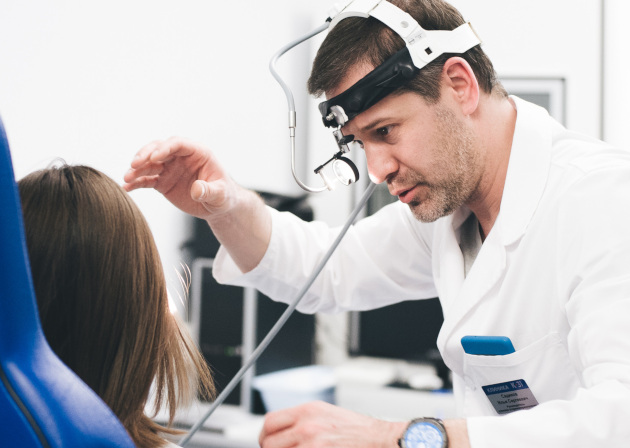
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
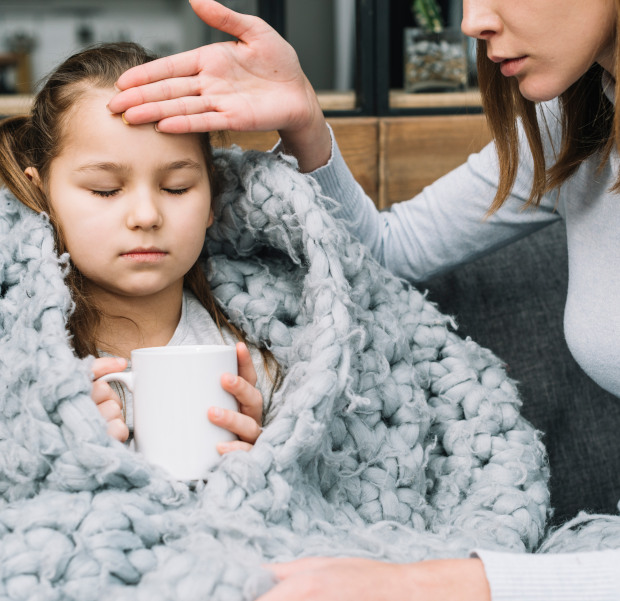
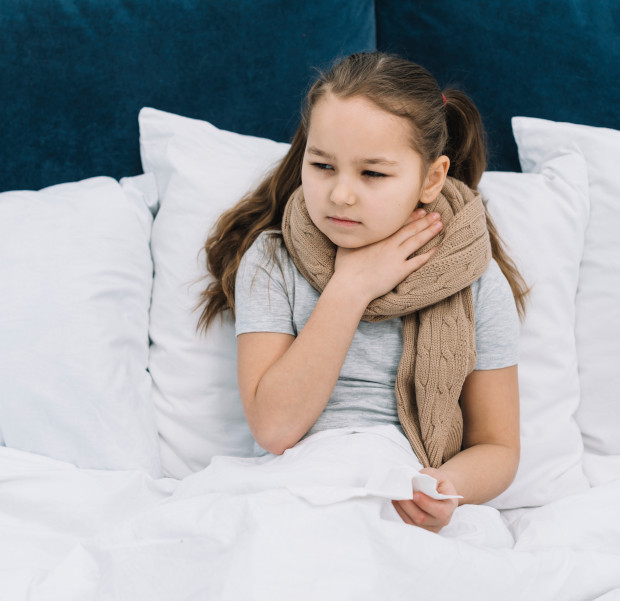
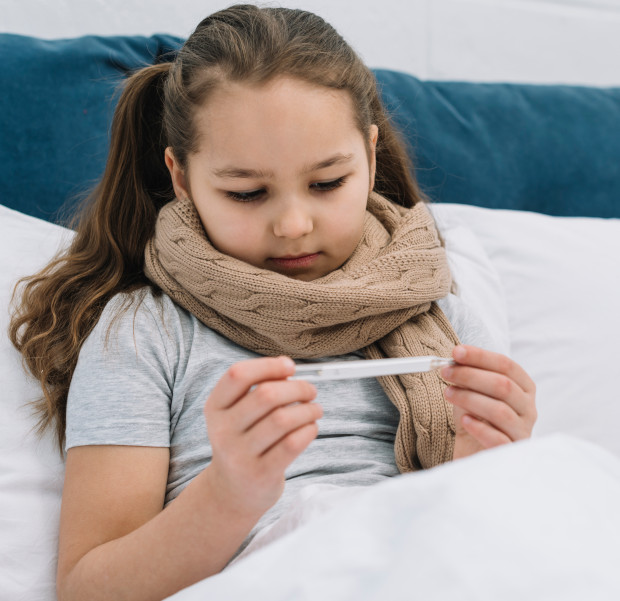
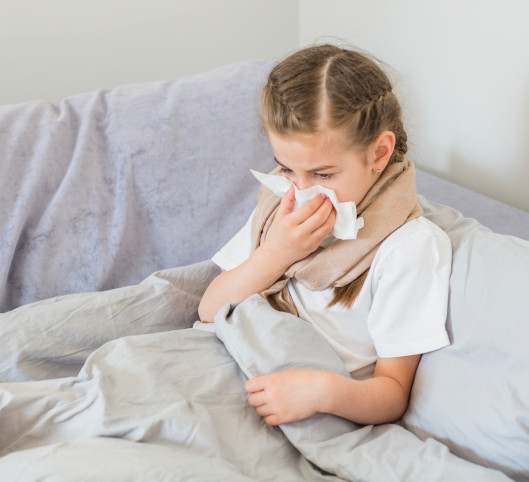












































Causes of sore throat in children
In 80% of cases, the main cause of childhood sore throat is a bacterial infection (or virus). The causative agent of the disease in children of primary school age is often β-hemolytic streptococcus of group A. In 10% of cases, the cause of the development of pathology is Staphylococcus aureus. Mixed infection, pneumococcus and Haemophilus influenzae can also cause tonsillitis.
Predisposing factors for the development of angina are vitamin deficiency and changes in regional and general immunity during hypothermia. Traumatic tonsillitis develops against the background of surgical intervention in the nasopharynx and posterior parts of the nasal cavity. The endogenous form of the disease often progresses with caries and sinusitis.
Treatment of infectious (and any other) sore throat in children is prescribed by identifying symptoms.