Endoscopy of the throat and larynx (laryngoscopy)

specialists

equipment

treatment
Types of laryngoscopy
Direct laryngoscopy
Direct laryngoscopy involves examining the larynx using a special instrument - a laryngoscope. This tool can be flexible or rigid. A flexible laryngoscope is a thin, flexible tube with a light source at one end (its use allows you to examine the larynx more conveniently and safely). A rigid laryngoscope is quite rigid. It is more often used during surgical interventions.
Direct laryngoscopy is performed both using general anesthesia and local anesthesia (in order to reduce discomfort, the anesthetic is applied to the mucous membrane of the larynx). In some cases, vasoconstrictors are used to reduce mucus production.
This method is used to diagnose diseases of the hypopharynx and restore airway patency. Direct laryngoscopy is also performed in preparation for operations, when taking tissue samples for analysis, as well as when removing tumors.
The process looks like this:
- The doctor inserts the tip of the laryngoscope to the root of the tongue (with the patient's head slightly thrown back).
- The specialist lowers the laryngoscope lower, pressing the tongue to the bottom of the mouth.
- To examine the larynx, the doctor carefully moves the instrument towards the vocal folds.
The procedure is not performed for injuries to the cervical spine. It is not prescribed for acute inflammation, frequent attacks of epilepsy, narrowing of the airways, bleeding and serious cardiovascular diseases.
Indirect laryngoscopy
This method involves the use of a laryngeal mirror. The procedure is recommended for inflammation of the laryngopharynx. It is also prescribed in the presence of foreign bodies in the larynx, in the detection of infectious diseases, swelling and narrowing of the airways. Indirect laryngoscopy is not performed on children under 5 years of age due to the anatomical features of their respiratory system.
During the procedure, the doctor inserts a mirror into the patient’s oral cavity without touching the tissues and mucous membranes. (this helps avoid the gag reflex). To avoid fogging during the examination, the mirror is preheated.
The doctor asks the patient to open his mouth and stick out his tongue - the ENT doctor carefully grabs it with a sterile napkin and slightly pulls it down.
The otolaryngologist uses a headlamp to illuminate the larynx - this allows him to see the inside of the hypopharynx. In order to thoroughly examine all parts of the larynx, the doctor changes the angle of the mirror. Also, to get a better look at the larynx, he asks the patient to say “i” or “e” in a drawn-out manner. This opens the epiglottis and makes it easier to visualize the laryngeal structures in an inverted position.
Other methods
In order to study the condition of the larynx, other diagnostic methods are also used. In particular, retrograde laryngoscopy is used to examine the lower parts of the larynx. This method is especially relevant after tracheostomy. During this procedure, the doctor inserts a speculum through the tracheostomy opening directly into the trachea. Thus, he has the opportunity to examine the internal structures of the larynx from bottom to top.
Microlaryngoscopy provides the opportunity to look at areas of the hypopharynx that are inaccessible to other diagnostic tools. This method requires the use of specialized equipment with a high degree of resolution. Microlaryngoscopy is often used to detect and study malignant neoplasms in the larynx: this is due to its ability to visualize in detail the smallest details of the internal structure of the laryngopharynx.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
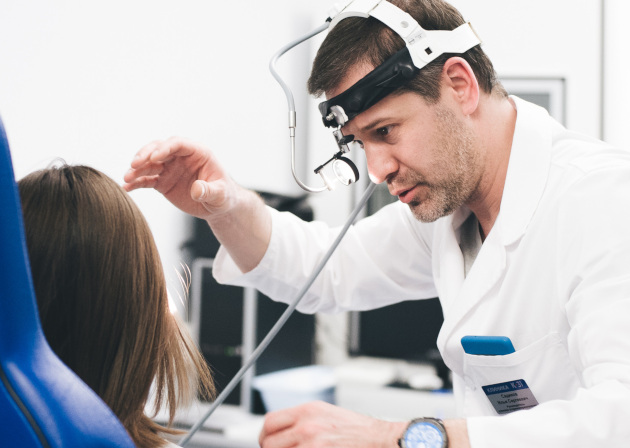
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services






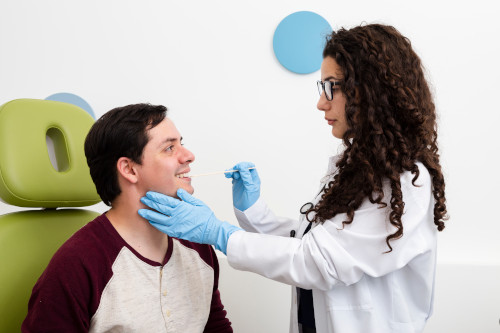
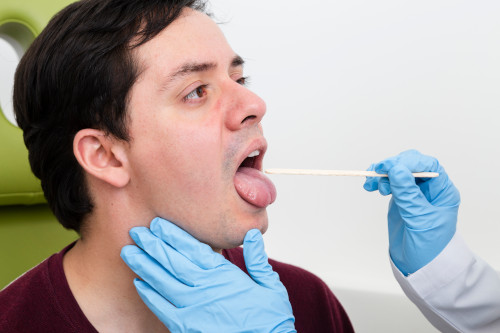



























How to prepare?
The examination is carried out on an empty stomach. The last meal should take place 8-9 hours before visiting the doctor (you only need to eat light food). These precautions help prevent the gag reflex during the procedure. In addition, this way you can eliminate the risk of vomit getting into the respiratory tract.
You should also notify the doctor about all medications the patient is taking and about possible allergic reactions to medications. Anticoagulants should be stopped 2 days before the examination. In addition, you must refrain from smoking before the procedure. Nicotine use increases the production of mucus and saliva. This not only causes coughing, but also makes examination difficult.