Endoscopic removal of a maxillary sinus cyst
Endoscopic surgery to remove a maxillary sinus cyst is the safest and most effective method for treating neoplasms, formed in the maxillary (maxillary) sinus. Often patients do not suspect the presence of pathology because it occurs asymptomatic and discovered by chance during instrumental diagnostics. Perform endoscopic removal of a cyst in the sinus nose at an affordable price at the K+31 clinic. Qualified and experienced doctors perform operations using modern equipment expert class, which guarantees high-quality and low-traumatic treatment.

specialists

equipment

treatment

The clinical picture depends on the size and location of the tumor. The main symptoms include:
- Permanent nasal congestion
- Pain, feeling of fullness in the upper jaw, under the eye or in the frontal part of the face
- Impaired sense of smell
- Accumulation of mucus in the throat and nasopharynx (especially in the morning)
- Feeling of a foreign body in the nose or sinus
- Swelling and redness of the mucous membrane
- Persistent or recurrent headaches, poorly relieved by analgesics
If the cyst is large enough, breathing difficulties may arise, especially during physical activity. Patients complain of discomfort when moving the eyeballs, increased pain when tilting the head to the sides or forward. Large tumors cause deformation of the maxillary sinus, causing the face to become asymmetrical. Constant pressure on tissues provokes microcirculation disorders and nutritional deficiencies. This leads to thinning of the sinus walls, increasing their fragility. When palpating the affected area, a characteristic crunching sensation is felt. If an infection gets into the paranasal sinuses, there is a high probability of fistula formation.
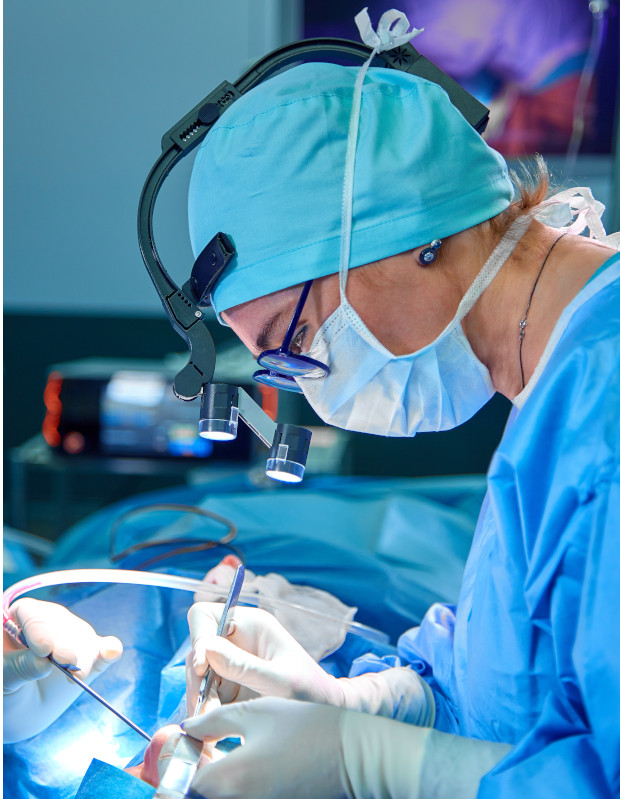
Surgical intervention consists of the following stages:
- Preparation. The patient is positioned on the operating table in a supine position with the head elevated for optimal access to the nasal passages and sinuses
- Pain relief. General anesthesia is usually used, but in some cases local anesthesia is used in combination with sedation
- Insertion of an endoscope through the nasal cavity to visualize the internal structure of the nose and maxillary sinus. The device is equipped with a camera, which allows the surgeon to observe the surgical field on a monitor in real time
- Antrostomia. The doctor makes a small hole in the anterior or lower wall of the maxillary sinus through the natural opening or expanding it with special instruments
- Removal of the cyst through the created hole. It is possible to use a microdebrider for careful processing of fabric
- Hemostasis. If necessary, stop bleeding using coagulation or tamponade
- Rinse the sinuses. After the tumor is removed, the sinus is washed with an antiseptic solution to remove tissue debris and prevent infection
Upon completion of the endoscopy, the doctor removes the device from the nasal cavity and transfers the patient to the recovery room for observation until complete awakening from anesthesia. Subsequently, follow-up examinations are carried out to assess the healing process. If necessary, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic procedures that allow a detailed study of the condition of the sinuses.

To identify a maxillary sinus cyst, the doctor first finds out the patient’s complaints, their duration and nature, the presence of chronic diseases, injuries to the nose and face, and also conducts a survey about past infectious diseases. Then he visually examines the nasal cavity and facial area to identify signs of inflammation, swelling, and deformation.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the following studies are required:
- General and biochemical blood test. Help assess the patient’s general health and detect signs of inflammation
- General radiography of the sinuses. Shows darkening in the area of the maxillary sinus, which may indicate the presence of a cyst
- Computed tomography. Allows you to obtain detailed images and accurately determine the size, location and structure of the tumor
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Used for differential diagnosis and assessment of soft tissue structures
If an infection or tumor process is suspected, material can be taken for cytological examination. It allows you to determine the nature of the contents and select an effective treatment plan. To rule out a dental cyst or periodontitis, a consultation with a dentist is necessary. If the patient has a history of allergic diseases, he is given a referral to an allergist.
Types of operations to remove maxillary sinus cysts
Endoscopic surgery
The most common method, since it provides less tissue trauma, quick recovery, no visible scars, and less risk of infectious complications. An endoscope is inserted through the nasal passages, with which the surgeon examines the maxillary sinus and removes the cyst. If necessary, after surgery, the doctor performs plastic surgery of the anastomosis.
Laser removal
Laser surgery involves removing the cyst using a laser beam. It destroys the neoplasm and evaporates its contents. The technique is characterized by rapid healing and minimal tissue trauma. Treatment with a laser beam is not suitable for large neoplasms, since their evaporation takes a long time.
Radical surgery (maxillary sinusotomy)
Traditional surgery in which an incision is made in the gum or face to access the maxillary sinus. Suitable for large tumors and complex cases. An incision is made in the gum area above the upper teeth or on the face, after which the surgeon gains access to the sinus and removes the cyst. There may be visible scars after surgery.
Microsinusrotomy
It is combined with endoscopic technology, which minimizes tissue trauma and speeds up the patient’s recovery. The surgeon makes a small incision (usually no more than 5 mm) in the wall of the sinus through the natural opening or expands it with microtools. The patient is under general anesthesia. After the intervention there are no scars or scars left.
Endonasal removal
Refers to endoscopic methods of surgical treatment. The surgery is performed through the nasal passages using an endoscope, which allows surgeons to get an excellent view of the surgical area without having to make large incisions in the face or mouth. Features of the method: lower risk of damage to nerves, blood vessels and adjacent organs, rapid recovery, minimal likelihood of complications.
Answers to popular questions
What are the possible consequences of cyst formation?
If left untreated, a sinus cyst can become infected and cause acute or chronic sinusitis. In rare cases, the infection spreads beyond the sinus and leads to the development of an abscess or osteomyelitis (if the infection has affected the bones of the facial skeleton). A neoplasm located close to the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw, causes pain and discomfort, exerts pressure, leading to their displacement.
What are the risks and possible complications after surgery?
Possible complications include bleeding, infection, damage to surrounding tissue, recurrence of the cyst, and postoperative symptoms such as a dry, crusty nose.
Is it possible to avoid surgery?
Yes. If the tumor does not cause symptoms and is not complicated, you can limit yourself to observation and conservative treatment.
How long is the surgery and recovery period?
The operation usually lasts from 30 minutes to 2 hours, depending on the complexity of the clinical case and the chosen technique. The recovery period after endoscopy ranges from 1 to 3 days, after maxillary sinusotomy - up to 2 weeks.
When is endoscopic cyst removal necessary?
Endoscopy is indicated in the presence of nasal congestion, infectious complications, large neoplasms, recurrent sinusitis, pain in the teeth of the upper jaw and ineffectiveness of conservative treatment.
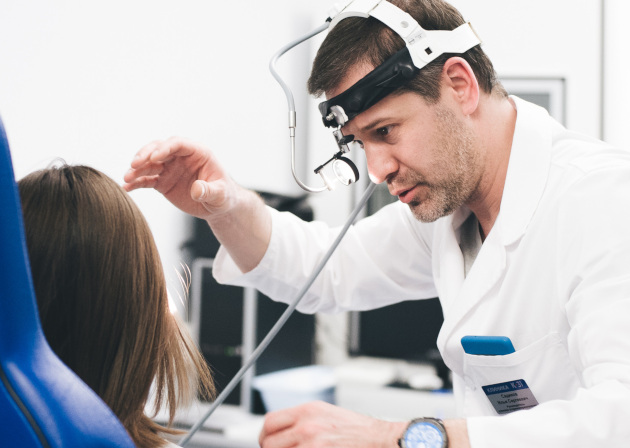
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services


































Causes of maxillary sinus cysts
A maxillary sinus cyst can form for the following reasons:
Sometimes a maxillary sinus cyst occurs in patients with systemic immune disorders. Its growth accelerates against the background of ARVI, local hypothermia and can reach more than 15 mm. The intensity of cyst growth in each case is individual and depends on the cause of development. To prevent complications, it is important to seek medical help promptly.