Cholesteatoma

specialists

equipment

treatment
Classification of cholesteatomas

There are two types of middle ear cholesteatoma:
- Innate (true)
- Purchased (false)
True cholesteatoma, also called “pearl tumor”, has the appearance of a smooth capsule and is formed during embryonic development. Cholesteatoma is most often localized in the temporal bone, but can also be found in other parts of the skull, including the brain.
False cholesteatomas develop against the background of prolonged inflammatory processes in the ear or after injury. Their formation is due to two mechanisms:
- The first, associated with the penetration of the epithelium of the external auditory canal into the middle ear through defects of the eardrum
- Second. Activated when there are problems with the Eustachian tube, leading to a decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity, subsequent absorption and accumulation of keratin in the membrane
These processes contribute to the accumulation of dead cells and the formation of pseudotumor.
Symptoms of cholesteatoma

At an early stage, cholesteatoma usually does not cause concern to patients and is detected incidentally during examination. As cholesteatoma increases in size, discomfort and pressure on surrounding tissues and organs increase.
Other symptoms of holistoma include:
- Headaches and dizziness
- Insomnia
- Deterioration of vision
- Constant pain in the ear area
- Purulent discharge from the ear
- Unilateral hearing loss
Hearing loss can range from subtle to significant. Usually it is of a mixed nature due to the effect on the hearing aid.
General information about the treatment of cholesteatoma
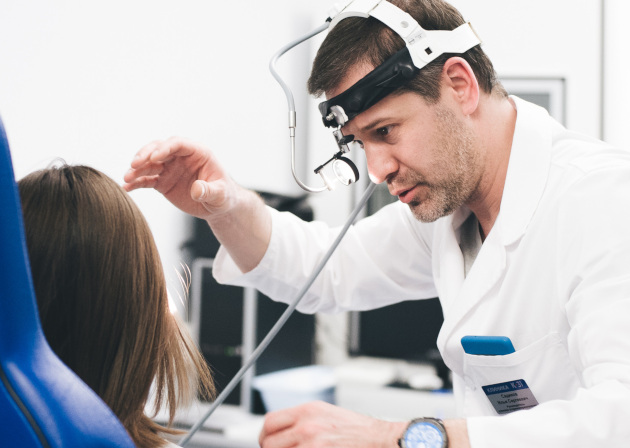
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Services

































What is ear cholesteatoma and the mechanisms of its development
Cholesteatoma is an encapsulated neoplasm that occurs in the epithelial layers of the middle ear. In 90% of cases, its appearance is associated with chronic purulent otitis. According to statistics, such a complication occurs in 0.01% of patients with this disease.
Other reasons for the formation of cholesteatomas include:
At risk are mainly children over 10 years old, as well as young people aged 20-30 years. The younger the patient, the more rapidly the disease progresses and causes frequent relapses.