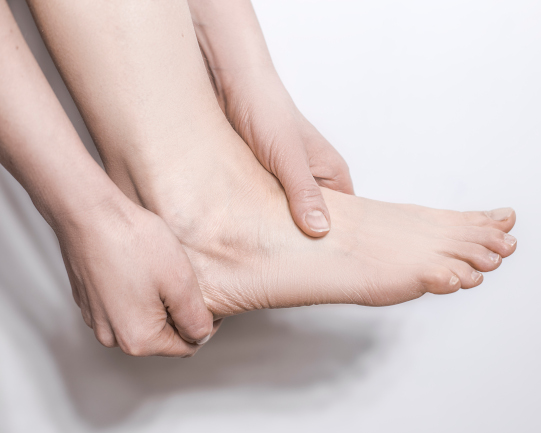
Diabetic foot
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of the endocrine system, which manifests itself in increased blood glucose levels due to insufficient insulin activity. According to the World Health Organization, The disease has been diagnosed in 425 million people, which is about 6.03% of the world's population. One of The most common complication of this condition is considered to be diabetic foot, affecting 20% of patients. Pathology occurs due to damage to nerve fibers and endings.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Classification
Depending on the mechanism of occurrence, the disease is divided into three main types:
- Ischemic. Occurs in 5-10% of cases. Associated with disorders of the vascular system
- Neuropathic. The most common type, which is detected in 70% of patients. Develops against the background of damage to the nervous system, mainly in the area of the feet
- Neuroischemic. Diagnosed in 20-30% of patients who live with diabetes for a long time. Combines signs of ischemic and neuropathic forms
To determine the degree of foot ulceration, doctors use the Wagner scale. They evaluate 3 main parameters - the depth of damage to the epidermis and muscle tissue, the presence of gangrene, the degree of infection.

Шкала Вагнера
According to the Wagner scale, the diabetic foot goes through several stages of development:
- Zero. There are no external signs, but diabetes has already been detected. During this period, the key task of the doctor is to prevent the development of the disease using preventive measures
- First. Characterized by the appearance of superficial ulcers that require complex treatment
- Second. Diabetic ulcers penetrate deeper, reaching the muscles and tendons, without infection. Therapy and prevention required
- Third. Associated with the appearance of deep, infected ulcers that reach the bone. Intensive treatment is required, including surgery
- Fourth. Necrosis of bones and tissues of the fingers occurs. Immediate surgical intervention is required
- Fifth. Gangrene of the foot develops, which entails amputation
The Wagner classification does not take into account the cause of ulcers and the nature of their infection. Among the most common infections are those caused by fungi, Escherichia coli bacteria, salmonella, streptococci, gonococci and other pathogens.

Signs of a diabetic foot
The symptoms of diabetic foot depend on the form of the pathology. Symptoms of the neuropathic form include:
- Insensitivity to pain due to injury
- Preservation of the natural color and warmth of the skin
- Decreased sensitivity at all levels of the periphery
- Permanent pulsation in the area of the feet
Neuropathic lesions most often occur in areas of greatest pressure on the foot - for example, between the phalanges of the toes or on the big toe. In these places, calluses and seals form due to hyperkeratosis, under which an ulcer forms.
Ischemic gangrenous foot is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Paling of the skin and decrease in its temperature
- Presence of sensitivity in the feet
- Arterial hypertension and dyslipidemia
The most characteristic and common symptom is acute pain.
Common signs of diabetic foot include:
- Spasms in the lower leg muscles
- Feeling of itching and tingling in the feet
- Fatigue in the legs
- The appearance of small vesicles with transparent contents on the skin of the feet
Patients at the diabetic foot office often experience problems such as fungal foot infections, excessive foot sweating, foot deformities, and limping when walking.

Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, the patient must undergo a number of instrumental studies:
- X-ray – reveals structural changes in bones
- Ultrasound bone density measurement - determines bone density
- Angiography using a radiopaque substance - allows you to detect abnormalities in the blood vessel system
- Peripheral computerized arteriography is a non-invasive method for assessing blood circulation in the legs
Another necessary procedure is Dopplerography of the vessels of the lower extremities. It identifies problems related to blood flow and vasoconstriction.
Laboratory diagnostic methods include:
- Biochemical blood test
- Clinical urine analysis
- Bacteriological examination to check for infections in ulcers
For a detailed diagnosis and choice of treatment for diabetic foot, additional consultations with an orthopedist, angiosurgeon, and phlebologist may be required.
Complications
One of the serious but rare complications is Charcot arthropathy. This condition is characterized by destruction of the bones and joints of the foot, significantly altering its shape and functionality. The main complications associated with diabetic foot include:
Infections Microtraumas heal very slowly, increasing the likelihood of infections.

Foot deformities. Due to nerve damage, muscle motility decreases, which leads to atrophy and changes in the shape of the foot, and the development of flat feet.
Gangrene Tissue necrosis, which in most cases requires amputation of the limb to prevent the spread of infection.
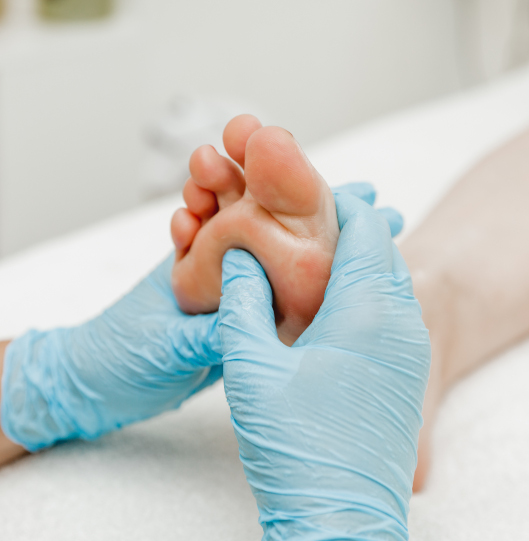
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other services
Plantar warts
Laser nail treatmentReviews 4













Mechanism of occurrence
Prolonged excess of blood glucose levels disrupts the functioning of blood vessels and the nervous system, increasing thereby the likelihood of infectious complications. Angiopathy (vascular dysfunction) contributes to the formation of atherosclerotic deposits, creating obstacles to normal blood flow. This leads to a decrease in blood supply to tissues, oxygen starvation and the appearance of leg ulcers. They first appear on the fingers, then spread to the feet, legs and thighs.
Decreased circulation is accompanied by decreased sensation in the legs due to neuropathy (peripheral nerve damage). Because of this, patients often do not notice minor injuries, which increases the risk of infection. A combination of compromised blood supply, nerve damage, and infection often leads to the development of diabetic foot.
In addition to the main cause of this syndrome, there are a number of factors that increase the risk of its development. Among them:
High-risk groups include people with visual impairments, the elderly, and patients drinking excessive amounts of alcohol. They are more likely to suffer foot injuries which may go unnoticed.