Treatment of an abscess (abscess) on the gum

specialists

equipment

treatment
Main symptoms
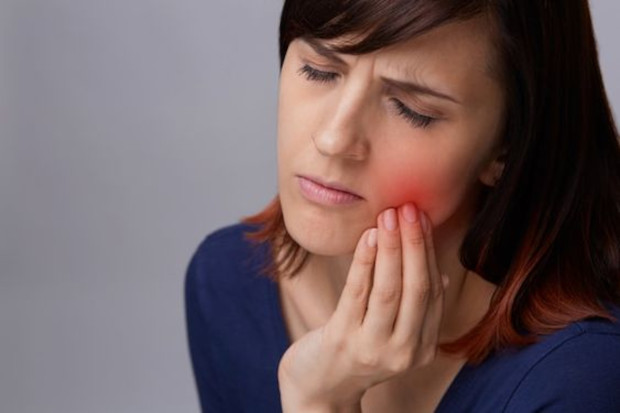

Symptoms of an abscess on the gum of a tooth depend on what pathology provoked its appearance. With periodontitis, an abscess on the gum appears as a small compaction. In some cases, a large purulent abscess forms, usually called a gumboil. Its development leads to more noticeable inflammation. Such swelling is often accompanied by dental (severe or moderate) pain when biting. If left untreated, swelling spreads to the soft tissues of the face.
An abscess that has formed under the mucous membrane of the gum against the background of periodontitis can burst, forming a fistula. This fistula connects to the source of inflammation at the root of the tooth, allowing pus to escape. When acute inflammation at the root of the tooth subsides and pus stops forming, the fistula openings heal until the next exacerbation.
If swelling appears on the gum, and the tooth looks healthy and does not have fillings, this indicates periodontitis, not periodontitis.
Diagnostic methods
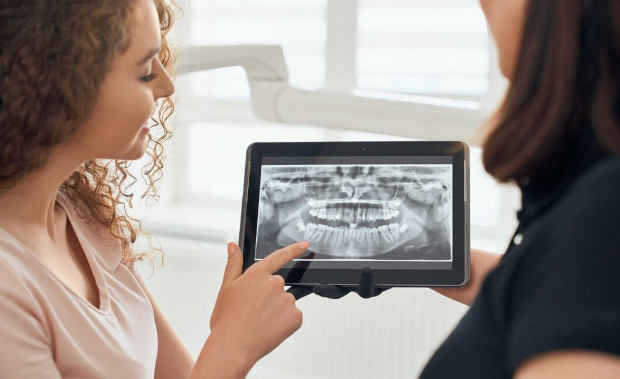
To establish the cause of gum suppuration, an integrated approach is used. First of all, the doctor interviews the patient and finds out when and how the symptoms arose. The dentist then carefully examines the gums, the area around the affected tooth, and other potential sources of infection. Particular attention is paid to areas with swelling and redness of the mucous membrane.
After this, the specialist sends the patient for an x-ray. This is necessary to identify inflammatory processes in the root area. The image will also help assess the condition of previously installed fillings in the canals. Unfortunately, about 60-70% of such fillings are installed incorrectly - this often leads to dental problems.
Treatment methods for gum abscess: how to remove pus from the gums
Treatment methods for gum abscess vary depending on its cause. During an exacerbation of chronic periodontitis, characterized by the formation of an abscess on the gum, the doctor usually removes the problematic tooth.
In some cases, however, treatment is carried out. In particular, therapy is prescribed if the root canals of the problem tooth are not filled. In this case, the dentist performs mechanical treatment of the canals and treats inflammation at the apex of the root.
Additionally, antibiotic therapy is prescribed and antiseptic rinses are performed. In difficult cases, in order to improve the outflow of pus, surgical intervention is prescribed. To remove pus from the gums, an incision is made under local anesthesia. Depending on the volume of the abscess, the incision size varies from 5 to 15 mm. After opening the abscess in the gum, a drain is inserted into the wound. This is necessary to prevent the accumulation of pus.
If the root canals were filled poorly, the doctor chooses between standard therapeutic treatment, which involves unsealing the canals and surgery - resection of the root apex. When treating an abscess on the gum, opening a periodontal abscess is also performed under local anesthesia. After this, antibiotic therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed.
Treatment of an abscess on the gum during periodontitis begins with eliminating the traumatic factor, for example, the overhanging edge of a filling. After this, the abscess is opened and the pocket is washed. In cases of deep inflammation with pus on the gums, root canal treatment is often required. The essence of the therapy is open curettage of the periodontal pocket and filling it with bone material.
For abscesses on the gums associated with tooth mobility, splinting is required. This procedure involves fixing a mobile tooth to adjacent stable teeth.

Modern methods of diagnostics and dental treatment at "K+31"
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Other Services
Plastic surgery of soft tissues of the oral cavity
Tooth extractionTreatment of inflammatory diseases
Treatment of stomatitis Gum treatment Treatment of gingivitis Treatment for gum recession GumplastyPlastic surgery of the frenulum
Treatment of alveolitis Wisdom tooth removal Bone grafting CBCTOnline consultation with a dental surgeon




















































Causes
An abscess on the gum near a tooth often forms against the background of chronic periodontitis. Due to the penetration of infection into the root canals of the tooth, a purulent focus forms at its apex. Dentists call such lesions granulomas or cysts. Often their presence goes unnoticed for many years. However, when chronic inflammation worsens, purulent abscesses form on the gums in the area of these lesions.
Another reason for the appearance of a white pustule on the gum is the development of periodontitis. This pathology can be local and generalized. The process in both cases develops in the periodontal pocket - the space between the gum and the surface of the tooth root. A gum abscess due to periodontitis is usually a small, swollen, and red area.