Tracheostomy

specialists

equipment

treatment
Types of tracheostomy surgery
There are several types of tracheostomy. Modern clinics perform planned, emergency and percutaneous surgeries.
Elective tracheostomy
The elective procedure is performed under controlled conditions. A tracheostomy tube is installed for chronic respiratory diseases and against the background of prolonged use of a ventilator. Intervention is not performed against the background of uncontrolled coagulopathies and the presence of infections.
Recovery after elective surgery is usually easier. This is due to the fact that the operation is performed under optimal conditions and with minimal stress for the patient.
Emergency tracheostomy
This procedure is performed in case of emergency conditions. In particular, it is indicated for:
- Severe blockage of the respiratory tract
- Anaphylactic shock
- Severe injuries to the larynx
Intervention is contraindicated if alternative, less invasive methods of restoring breathing are available. Due to the urgency of the procedure and possible complications, recovery takes longer.
Percutaneous tracheostomy
This is a less invasive method of performing the operation. This intervention is used in the intensive care unit. In particular, tracheostomy is performed on those patients who require long-term ventilation. Intervention is contraindicated in case of anatomical abnormalities of the neck and skin diseases at the site of intended access.
Surgery is performed under local anesthesia using an endoscope, which helps determine the exact location for insertion of the valve. During the process, the doctor makes a small puncture in the throat through which a tube (drainage) is inserted.
The main advantage of the percutaneous technique is the reduced risk of infections and bleeding. Its advantages also include reduced pain after surgery and a shorter rehabilitation period.
Types of tracheostomy installed
Tracheostomy tubes (cannulas) are intended to support breathing through an artificial lumen in the windpipe. These pipes differ in material, size and the presence of additional elements (cuffs, valves).
Tracheostomy placement procedure
Fixation of a tracheostomy requires the use of special medical instruments and strict adherence to technique. The tracheostomy process looks like this:
To make sure that air passes freely through the drainage, auscultation (listening) of the lungs is performed. In order to visually assess the correct location of the catheter in the throat, fiberoptic bronchoscopy is used.
Answers to popular questions
People often ask about what a tracheostomy is and what effect it has. They are also interested in caring for a tracheostomy tube and the features of living with it.
What is the difference between tracheotomy and tracheostomy?
Tracheotomy is the surgical process of creating an opening in the trachea. It allows temporary access to the airway. A tracheostomy is the placement of a special tube into this opening for long-term use.
Tracheotomy is mainly aimed at short-term solution of breathing problems. A tracheostomy provides continuous ventilation.
How often should a tracheostomy tube be changed?
Can I eat and drink with a tracheostomy tube?
How to live with a permanent tracheostomy?
Life changes quite a lot after installing drainage. For example, difficulties arise with going outside and with hygiene procedures: in cold weather you should stay at home, and you should only take a shower wearing a special mask. Periodically (the time interval will be determined by the doctor) it will be necessary to do inhalations.
In addition, a person with a tracheostomy needs special Velcro fasteners. They are easy to put on and take off and easy to care for.
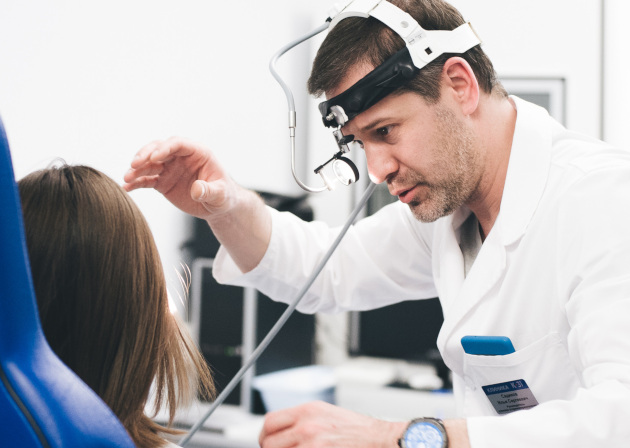
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price






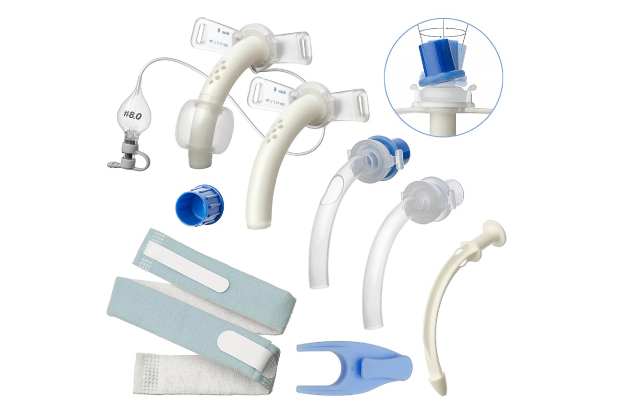
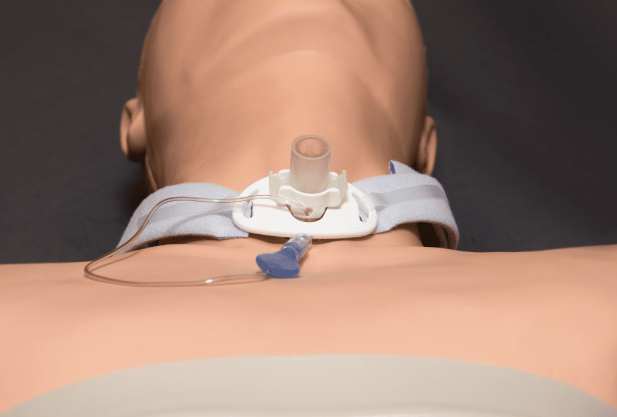

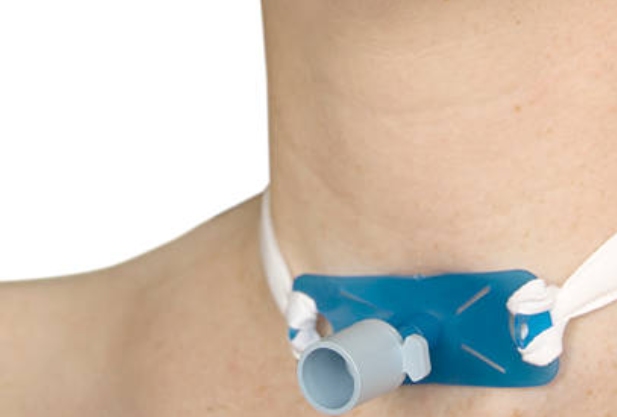
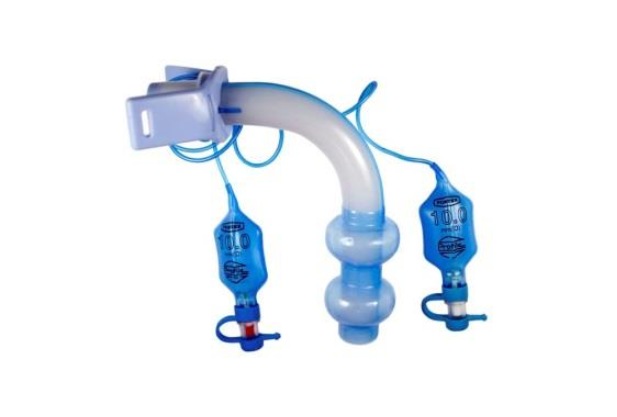




























What is a tracheostomy?
A tracheostomy is a procedure in which an artificial opening is created in the trachea (the main breathing tube). The operation is performed to provide an alternative path for air. It is prescribed if the upper respiratory tract is blocked or damaged.
The opening created in the trachea is called a tracheostomy. It can be temporary or permanent (the latter option is relevant if the patient requires long-term assistance). A temporary tracheostomy is often used during recovery from injuries, surgeries, or acute illnesses.
The intervention becomes a necessary measure in cases where the airways are blocked by tumors (for example, due to oncology of the larynx and vocal cords). This allows air to flow directly into the lungs, bypassing the damaged areas.
In addition, a tracheostomy is necessary for patients who require long-term support for artificial ventilation of the lungs. In particular, the installation of a tracheostomy tube in the trachea is performed against the background of severe neurological or respiratory conditions, in which independent breathing becomes impossible.
The procedure is performed under general anesthesia and in most cases has no direct contraindications.