Laryngeal stenosis

specialists

equipment

treatment

Causes of acute laryngeal stenosis in adults
- Allergic reactions to food
- Complications after a sore throat, flu or diphtheria
- Presence of tumors
- Throat injuries, burns
Causes of acute laryngeal stenosis in children

Acute throat stenosis in children is caused by the following factors:
- Congenital malformations, such as poor development of the respiratory muscles
- Prolonged use of mechanical ventilation devices, which leads to damage to the respiratory tract
- Infectious diseases (parainfluenza viruses, scarlet fever, measles and a complicated form of chickenpox)
Another reason is the structural features of the respiratory tract in children. In children, the larynx has a conical shape, is shorter and has a narrow lumen, which increases the risk of stenosis. Active work of the mucous glands can aggravate the situation. Even a minor inflammatory process causes a noticeable narrowing of the airways and makes breathing difficult.
General information
Treatment methods for narrowing of the glottis

The treatment regimen for laryngeal stenosis depends on the factor that provoked the narrowing of the throat.
In case of an allergic origin of the disease, doctors prescribe intravenous corticosteroids. For injuries and abscesses, surgery is required. For laryngeal stenosis of degrees 2 and 3, inhalations with adrenaline, intramuscular injections of dexamethasone, or the use of drugs for inhalation through a nebulizer are prescribed. If there is a threat to life, the patient is transferred to intensive care, where intubation or tracheostomy is performed to restore patency of the airway.

If laryngeal stenosis in adults occurs against the background of acute respiratory viral infection, therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of a cold. The course includes:
- Inhalations with soda
- Anti-inflammatory and painkillers
- Desensitizing drugs
At high temperatures, the use of specialized antipyretics is recommended.
Important! If the condition worsens significantly, more intensive treatments are needed, such as inhaled epinephrine, bronchodilators and oxygen therapy to reduce the load on the respiratory system and make breathing easier.
To strengthen the body's defenses, drugs that stimulate the production of interferon (Kagocel) and immunomodulators, for example, Polyoxidonium, are used. These drugs help to quickly relieve symptoms and increase interferon levels, providing a long-term protective effect.

For stage 1 laryngeal stenosis, outpatient treatment is possible. Therapy involves the use of anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs, diuretics to reduce swelling, as well as methods to facilitate breathing and reduce hypoxia. These include inhalation of humidified oxygen or medications, as well as special breathing exercises to improve ventilation.
For adults with developed laryngeal paresis after surgery and in the absence of respiratory failure, conservative treatment is provided. It involves taking antibiotics, hormonal and angioprotective drugs, as well as drugs to improve metabolism and neuroprotection.
Physiotherapy procedures also play an important role in restoring the functions of the larynx. To restore the functions of the larynx, UHF therapy and electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory and regenerating drugs are indicated.

Treatment of stenosis in a child
Stenosis in children is a serious condition that requires a careful and competent approach to treatment. Depending on the degree of the disease, stenosis in a child can manifest itself with various symptoms, ranging from mild difficulty breathing to critical life-threatening conditions.
To begin with, it is important to establish the causes of stenosis in the child. In the case of an acute form of the disease, doctors most often resort to prescribing corticosteroids and anticholinergic drugs aimed at relieving inflammation and swelling. Laryngeal stenosis in children is often accompanied by hypoxia, so after stabilization of the child’s condition, humidified oxygen inhalations are prescribed.
Important! Symptoms of laryngeal stenosis in a child can significantly worsen the quality of his life, so do not delay contacting a doctor.
If the disease is mild (1st degree stenosis in a child), then treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. In more severe cases, hospitalization is necessary. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and antihistamine drugs, mucolytics and alkaline inhalations are used for treatment. For bacterial infections, antibacterial agents are used.
Pay attention! If conservative treatment does not bring the desired result or in case of acute asphyxia, surgical intervention is required.
For children over 8 years old, puncture conicotomy is indicated. For chronic scarring laryngeal stenosis in children, treatment may include endoscopic operations such as balloon dilation or laser microsurgery.
After treatment of stenosis, the child begins an equally important stage - rehabilitation. He is recommended to have a gentle regimen, regular examinations by an ENT doctor and avoidance of vocal stress. It is important to limit the consumption of foods that can irritate the throat mucosa.
Stenosis in laryngitis

Stenosis with laryngitis is a serious complication that occurs as a result of an acute inflammatory process in the larynx. This condition is especially dangerous for children, since their airways are narrow, and even minor swelling causes significant breathing difficulties.
Treatment for stenosis should begin as early as possible to prevent the development of serious complications. For grade 1 and 2 stenosis, treatment of laryngitis is usually conservative and includes inhalation, the use of anti-inflammatory and expectorant drugs, as well as corticosteroids to reduce swelling of the mucous membrane. It is important to provide moist, cool air to reduce swelling and improve breathing.
For grade 3 stenosis, when there is significant narrowing of the airways, hospitalization and oxygen therapy may be required. In critical cases where upper airway stenosis and intrathoracic airway stenosis develop, surgery is performed to ensure airway patency.
In children, stenosis due to laryngitis is often accompanied by a strong cough, which is characterized by a rough “barking” sound. This is due to inflammation and swelling in the larynx area, which leads to a narrowing of the airways.
Acute laryngitis with laryngeal stenosis can progress rapidly, especially in young children. Early initiation of treatment helps to avoid the progression of the disease to a more severe form and the development of complications.
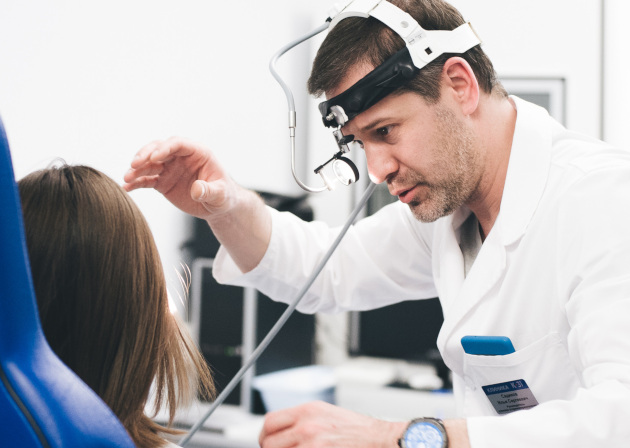
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
Photo gallery K+31

































About the disease
Laryngeal stenosis is a pathological narrowing of the lumen of the larynx, which prevents the normal passage of air through the respiratory tract. The development of the disease is most often preceded by inflammatory processes, trauma, and infection. Acute laryngeal stenosis manifests itself in the form of difficulty breathing, changes in voice, or a feeling of shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
Treatment depends on the cause and extent of the stenosis and may include medications, surgery, or specialized breathing apparatus.