Paranasal sinus cysts

specialists

equipment

treatment
Symptoms of a sinus cyst

The following symptoms occur most often:
- Discomfort in the upper jaw, pressure on the eye.
- Recurrent or constant headaches.
- Mucus running down the back of the throat.
- When diving to depths or sharp ascent, headaches appear or intensify.
- When the cyst is localized in the sphenoid sinus, complaints characteristic of sphenoiditis are possible.
Complaints depend on the location and size of the cyst and the structure of the maxillary sinus.
Diagnosis and treatment of paranasal sinus cysts

X-ray methods are used for diagnosis. The most optimal is CT (computed tomography) of the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses, which allows you to determine the size of the cyst and its location with millimeter accuracy.
Treatment of cysts in the paranasal sinuses is possible only with the help of surgical methods. Today, the gold standard of surgery is the use of endoscopic techniques in combination with the FESS technique. In the Otorhinolaryngology Department of the K+31 Clinic, endoscopic instruments are used, which allows the doctor to monitor the entire progress of the operation on the monitor in real time and see the microstructure of the nose. The operation is performed through the nose, which helps avoid incisions on the face. The method has virtually no contraindications, rarely has complications, reduces the time of hospital stay (patients are discharged on the same day) and allows you to return to the normal rhythm of life as quickly as possible.
General information about treatment
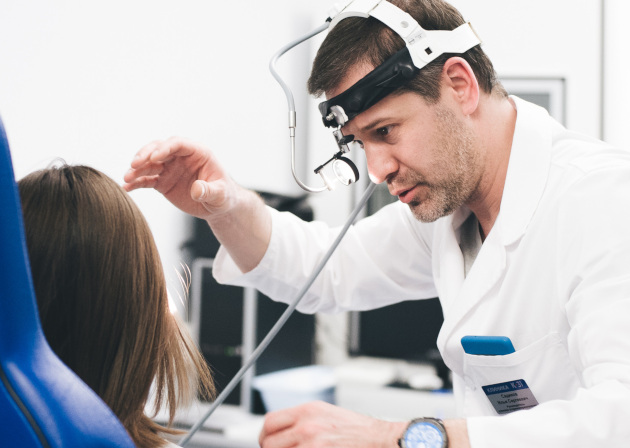
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price
































About the disease
A sinus cyst is a formation with thin and elastic walls, which is filled with fluid from the inside. The size and location of cysts in the sinus may vary. As a result, the manifestations of cysts may vary from patient to patient.
Inside the mucous membrane, humans have special glands that produce mucus throughout a person’s life. The glands have their own excretory ducts that open onto the surface of the mucous membrane. If, due to an inflammatory process (or for another reason), the gland duct closes, then it stops working, but mucus continues to be produced. The mucus does not find a way out, the walls expand under pressure, which leads to the formation of a spherical container. Most often, cysts form in the area of the maxillary sinuses.