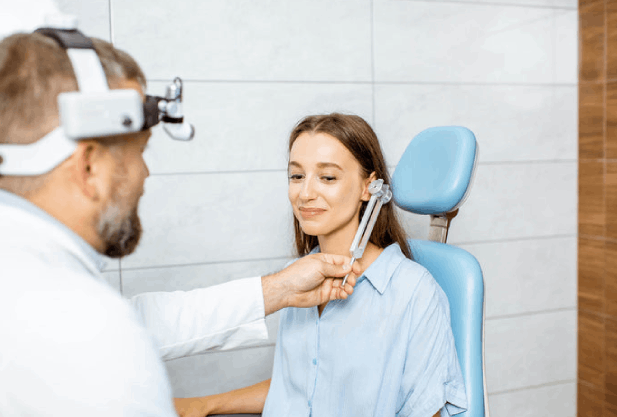
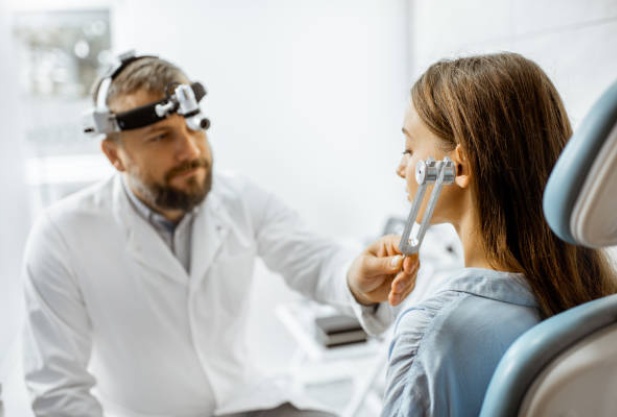
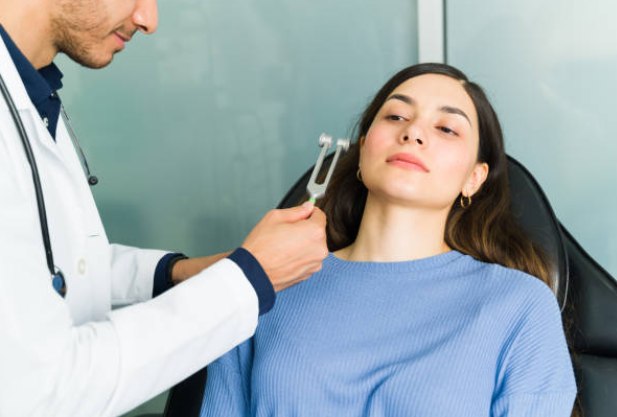
Hearing test using a tuning fork

specialists

equipment

treatment
Indications for tuning fork examination
Research using multi-frequency tuning forks allows us to determine the nature and type of hearing damage. During the examination, the doctor uses special medical tuning forks. With their help, hearing sensitivity is assessed and sound conduction through the air and bone structures of the patient is analyzed.
People who work in noisy environments or frequently attend loud events also need a hearing test. In addition, people who have a history of hearing loss in their family should be examined.

A tuning fork is used in the following cases:
- If you suspect hearing loss The first sign that your hearing is deteriorating is difficulty understanding speech. In this case, the person has to constantly ask again and increase the volume of the TV.
- After injury It is imperative to see a doctor after severe blows to the head resulting from a fall or accident.
- With age-related changes With age, hearing abilities deteriorate. A tuning fork study helps determine the level of these changes.
Indicators and research
Verified indicators
Each indicator being checked has its own range of values. More detailed information about this is presented in the table.
|
Indicator |
Description |
Unit |
Possible indicators |
|
Sound conduction through air |
Evaluation of the hearing aid's ability to perceive sounds transmitted through the air. |
Decibels (dB) |
Normal: 0-25 dB; Reduced: 26-40 dB; Moderate reduction: 41-55 dB; Heavy reduction: >55 dB |
|
Sound conduction through bone |
It checks how well the skull bone conducts sounds. This helps rule out or confirm the presence of problems in the middle ear. |
Decibels (dB) |
Normal: 0-25 dB; Reduced: 26-40 dB; Moderate reduction: 41-55 dB; Heavy reduction: >55 dB |
|
Balance between ears |
Comparison of the hearing function of both ears. Sometimes hearing problems are observed only on one side. This is usually due to injury or an infection that affects only one ear. |
Without one |
Symmetrical; Asymmetric |
|
Response to different sound frequencies |
It is intended to study the ability to perceive high, medium and low frequencies. |
Hertz (Hz) |
Low: 250-500 Hz; Mid: 1000-2000 Hz; Treble: 4000-8000 Hz |
|
Hearing threshold |
It is intended to determine the minimum volume at which the ear is able to detect sound. |
Decibels (dB) |
Audibility: ≤25 dB; Reduced audibility: 26-40 dB; Hearing loss: >40 dB |
Air conduction hearing testing
During a tuning fork hearing test, the doctor lightly hits the device. At the same time, the tuning fork makes a vibrating sound. The specialist then places the device at some distance from the patient's ear. In this way, the doctor tests the patient’s ability to perceive and distinguish sounds at different volume levels and tones. The patient's task is to report whether he hears the sound. He should also tell the doctor when hearing becomes worse.
In this way, a tuning fork test helps determine how well the outer and middle ears are working. If the patient does not hear sound, this indicates a blockage in the ear canal or a problem with the eardrum.
Bone conduction hearing test
Bone conduction testing tests how effectively the bones of the skull transmit sound waves directly to the inner ear. To do this, the doctor activates the instrument and applies it to the mastoid - a bony protrusion located directly behind the auricle.
The patient must be told whether he hears the sound. This test allows your doctor to determine how well your inner ear and auditory nerve are functioning. If the test results show that bone conduction is better than air conduction, this indicates the development of otitis media or perforation (perforation) of the eardrum.
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price