Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane and lymphoid membrane of the posterior wall of the pharynx. It has acute and chronic forms. The nature of the disease is most often bacterial or viral. It often occurs in combination with tonsillitis. With modern diagnostic methods available at the K+31 clinic, the disease is highly treatable.

specialists

equipment

treatment

The disease in its chronic form can develop quite slowly. Remission can unexpectedly change to an acute phase and the reason for this is colds, hypothermia, viral infections, etc., which contribute to a decrease in human immunity. Symptoms may vary and depend on the form and type of disease.
With catarrhal form there is a sensation of a lump or foreign object in the throat, dryness, soreness, as well as a slight burning sensation when inhaling cool or, conversely, very warm air.
TheHypertrophic form is characterized by an increase in the volume of lymphatic tissue and thickening of the pharynx itself. Mucus and pus accumulate in the area of the back wall, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of a repulsive, pungent odor from the mouth. In addition, the symptoms are: a dry cough with pharyngitis, which cannot be treated with conventional medications, and a sore throat.
The most severe form is considered to be atrophic. The disease is characterized by sclerosis of the lymphoid system, submucosal layer and the mucosa itself, which rapidly progresses. Symptoms are: accumulating viscous secretions, the appearance of dense crusts, soreness and dry cough.
Among other things, patients complain of weakness, general deterioration of health, and fever. On examination, the submandibular lymph nodes become painful and enlarged.

Signs of acute pharyngitis are:
- Cough, which can develop into bronchitis.
- Rhinitis.
- Rash on the body.
- Stingling, tingling and sore throat when swallowing.
- Hoarseness.
- Increase in body temperature.
- Pain in joints and muscles.
In addition, there may be signs of intoxication of the body. In this case, emergency hospitalization is necessary.
Causes
The disease can occur for a number of reasons. Most often this occurs due to viral and infectious diseases, as well as cold air entering the throat, hypothermia, and a decrease in immunity.
In children
In a child, the disease is most often very severe. With a temperature of up to 39 degrees, acute pain in the throat due to pharyngitis, lethargy and weakness. The causes of the disease are usually bacterial and viral infections:
- Staphylococcus
- Various stamps of the flu virus.
- Adenovirus.
- Cytomegalovirus.
- Meningococcus
- Parainfluenza.
- Coronavirus.
- Rhinovirus.
- Streptococcus
- Haemophilus influenzae infection and others.
In addition, illness in a child can occur due to hypothermia, chronic rhinitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis or adenoiditis, throat injury, allergic reactions, hot liquid, acid or alkali.
Vomiting, frequent regurgitation, hernia and reflux of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm can also cause pharyngitis. The throat is irritated by the aggressive acid thrown into it from the stomach.
In adults
In addition, reasons include:
- Smoking.
- Consumption of alcoholic beverages.
- Inhalation of polluted air.
- Decreased immunity.
- Viral diseases.
- Injuries.
- Fungi.
- Staphylococci, streptococci.
- Sinusitis and rhinitis.
- Allergic reactions.
- Dental problems, such as caries.
In the chronic stage, the disease can worsen due to hypothermia, stress, physical and mental stress.
During pregnancy
As in other cases, the causative agents of pharyngitis in pregnant women are various viruses, bacteria, infections and fungi.
Also the cause may be: caries, incompletely cured acute respiratory viral infections, ENT diseases, caries, drinking too cold, inhaling hot or, conversely, cold air, passive smoking, etc.

- In no case should you engage in self-treatment for pharyngitis. The disease quickly turns into a chronic form, the further treatment of which becomes significantly more difficult.
- At the first signs of illness, you should contact a specialist. Only a competent physician will be able to correctly diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
- The medical center “Clinic K+31” has all the equipment necessary for diagnosis, and its specialists have the experience that makes it possible to recognize the disease even in the early stages and reduce the risk of complications to a minimum.
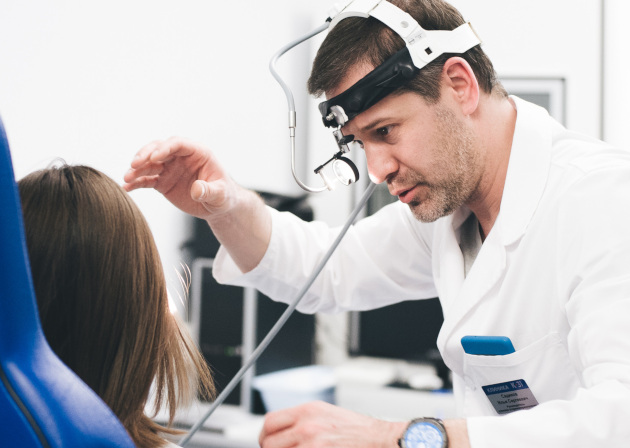
How is an appointment with an otolaryngologist at K+31?
Our doctors

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date
Price





























Symptoms of pharyngitis
There are several signs of pharyngitis that indicate the occurrence of the disease:
When examined by a specialist, redness of the pharynx and enlargement of the palatine tonsils are most often detected. The mucous membrane itself looks loose.
The symptoms of allergic pharyngitis are complemented by heat in the throat, as well as a feeling of the presence of a foreign body, which you want to get rid of by coughing. In addition, there is a hoarseness in the voice.