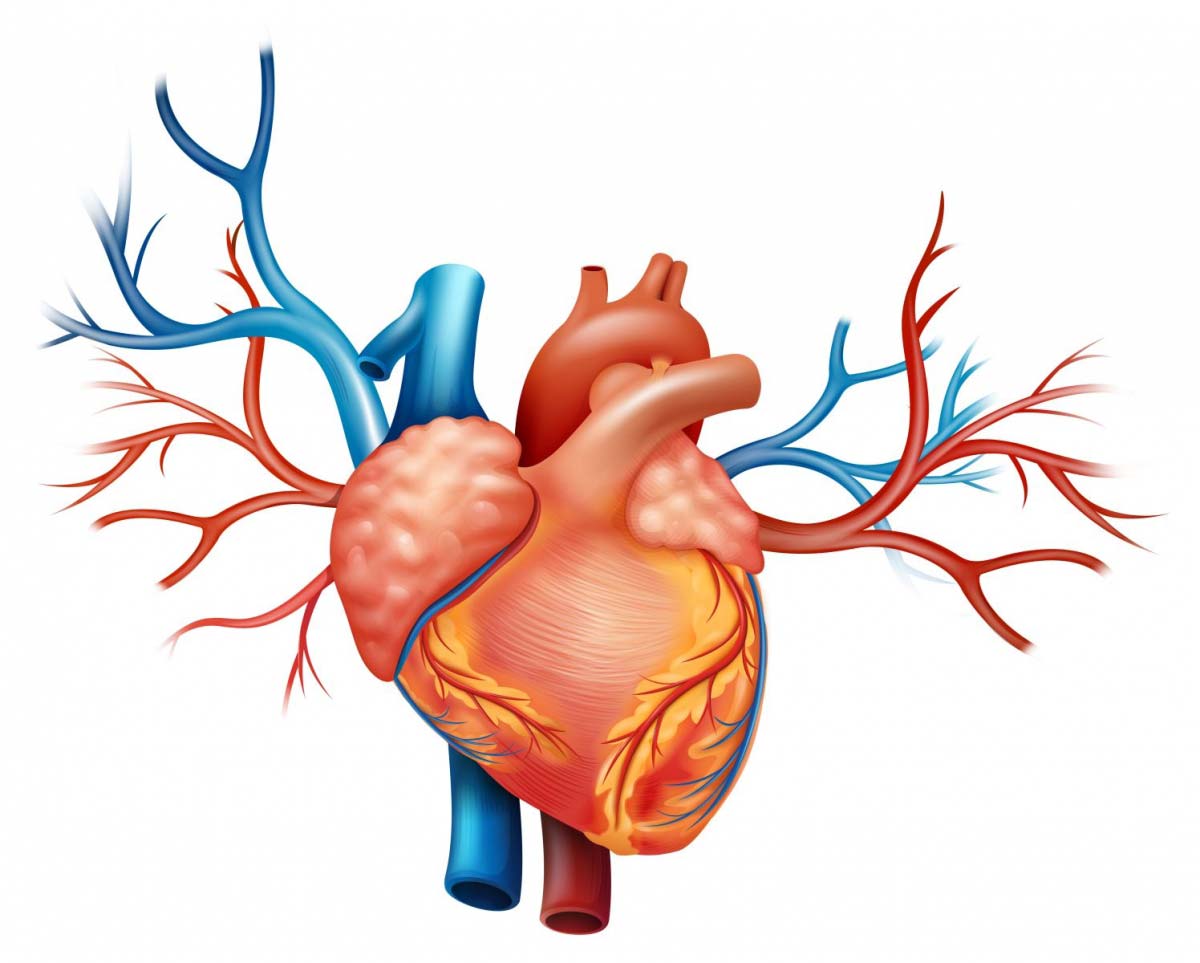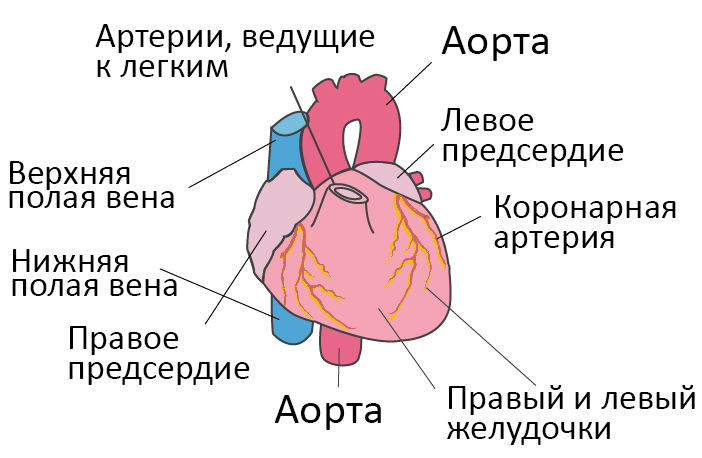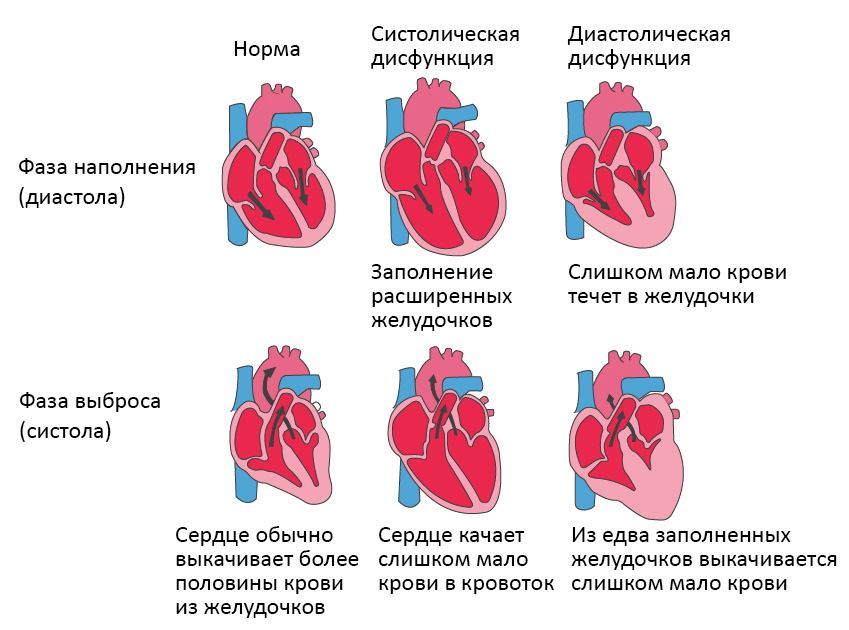
Heart failure (HF) is a complex of disorders caused mainly by a decrease in the contractility of the heart muscle.
Heart failure can be caused by various heart diseases, including coronary heart disease, cardiomyopathy, or post-infarction changes. At the same time, the myocardium is not able to develop proper efforts to expel blood from the left ventricle. There may be a situation where the myocardium is initially healthy, but there are obstacles to the movement of blood ejected by the heart, such as narrowing of large vessels, arterial hypertension, heart valve defects, etc.
In all these cases, it is difficult to expel blood from the left ventricle, which causes an increased load on the myocardium. To cope with increased stress, the heart muscle hypertrophies (thickens), begins to beat more often and for some time maintains normal blood circulation. Then the compensatory capabilities of the myocardium are depleted, irreversible changes develop in it - the replacement of muscle cells with connective tissue, which is not capable of contracting. The clinical picture of chronic heart failure begins to develop.