Treatment of wounds in diabetic foot
Risk assessment, prevention and treatment of diabetic foot syndrome, as well as concomitant diseases, using all the most effective techniques in the modern K+31 Lobachevsky clinic.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Причины развития заболевания

People with diabetes are at risk of developing diabetic foot syndrome due to elevated blood glucose levels. This excess sugar damages blood vessels and nerves, especially in the lower extremities. When blood vessels are damaged, blood cannot fully deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This disorder leads to poor wound healing and infections, sometimes resulting in leg amputation.
Nerve damage or neuropathy also plays a role, making the legs less sensitive to pain and pressure. This means that minor injuries or even ordinary pressure from shoes may not be noticed by the patient for a long time. This is why it is important for people with diabetes to regularly examine their feet and monitor their condition.
Symptoms and complications of diabetic foot

The clinical picture of diabetes mellitus can vary from minor skin lesions to deep trophic ulcers and purulent-necrotic processes. The most common symptoms include:
- Redness.
- Swelling
- Presence of open wounds or ulcers.
- Change in skin color.
- Burning sensation or pain in the foot.
Complications associated with diabetic foot can have serious health consequences and require timely medical intervention. The most significant of these include infectious processes that can progress to osteomyelitis - inflammation of the bone substance, often requiring surgical treatment. In addition, chronic diabetic ulcers and wounds on the foot that do not heal for a long time significantly worsen the patient’s quality of life. It becomes difficult for him to move independently and take care of himself.
Diabetic foot manifests itself in two main forms - neuropathic and ischemic, each of which has its own distinctive features.
When a person with diabetes develops neuropathy, which means damage to the nerves in the legs, the sensation in the feet becomes impaired. The skin becomes dry, leading to the formation of calluses.
Deformations of the feet and fingers, decreased reflexes and sensitivity can also be a sign of the neuropathic form, but they are not always noticeable at the initial stage. Due to decreased sensitivity of nerve endings, wounds and ulcers in diabetics often remain painless.
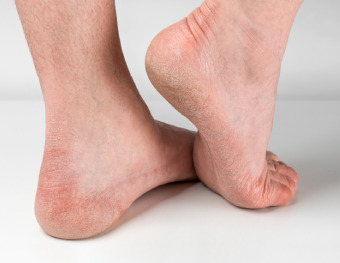
- Cold feet What indicates a circulatory disorder
- Dryness and flaking Dry skin, flaking, especially between the fingers
- Cracks Presence of cracks in diabetes.
- Pale and cyanotic color Pale or bluish skin, which is a sign of oxygen starvation of tissues
- Pain Painful ulcers and blisters on the legs due to diabetes, as well as pain when walking and stabbing sensations in the legs
- Special features Symptoms such as persistent pain, discoloration of the feet, and the appearance of ulcers on the legs in diabetes that do not heal for a long time should be of particular concern. These signs may indicate gangrene, which in advanced cases leads to amputation of the affected areas
Treatment of diabetic foot syndrome
Wound treatment for diabetes mellitus requires an integrated approach and the assistance of specialists from different medical fields. The endocrinologist, surgeon, cardiologist, neurologist and other experts work together to determine the best treatment plan. Most often, it includes both drug intervention and care and prevention measures.
Therapy principles include:
- The use of antibiotics and antimicrobials to fight infection.
- Improving blood supply to affected areas using vasoactive agents.
- Offload the foot to prevent further tissue damage.
- Local treatment of wounds in diabetes, including the use of antiseptics and wound-healing dressings.
Doctors pay special attention to the fight against infections. After receiving the results of bacteriological culture and antibiogram, they prescribe antibacterial therapy. It is important not only to suppress pathogenic microflora, but also to prevent the possible development of antibiotic resistance.
The second important area is the restoration of normal blood flow in the tissues of the foot. Vasoactive drugs help improve microcirculation, relieve ischemia and promote faster healing of wounds on the legs of diabetics.
Physical unloading of the foot is carried out using specially selected orthopedic shoes, orthoses or immobilizing bandages. This reduces pressure on the affected areas and prevents the formation of new lesions.
Local treatment of diabetic ulcers involves their regular treatment and the use of modern antiseptic and wound-healing agents, for example, atraumatic dressings, which promote rapid and high-quality healing of wounds in diabetes mellitus. The approach to the choice of local agents is individual and depends on the stage of the wound process and the presence of infection.
Stages of surgical treatment
Surgical treatment is a key method in the treatment of complicated stages of diabetic foot syndrome, when conservative methods do not give a positive result. It involves removing necrotic tissue, minimizing the risk of infection, and preserving the functionality of the limb.
Consultation and full examination by a surgeon
Carrying out diagnostic tests and analyzes
Development of an individual treatment plan taking into account the patient’s health condition
Consideration of possible surgical options
An operation that lasts on average about 30 minutes
Short-term postoperative observation in hospital
Receiving recommendations for further recovery
In extreme cases, when there is a threat to life, doctors may decide to amputate, which removes the source of infection and prevents its spread.
To preserve the tissue and support function of the foot as much as possible, doctors use techniques such as nerve decompression, correction of foot deformities, or excision of infected areas.
After surgery, it is important to follow the rehabilitation recommendations. Custom orthopedic shoes are an integral part of the postoperative period, as they help relieve the load on the operated foot and prevent new damage. Also, the recovery program usually includes diet, massage, exercise therapy and physical therapy.
Steps to care for diabetic foot wounds
Antiseptic wound treatment with products that do not contain alcohol or dyes. It helps prevent secondary infection and prepare the wound for further treatment.
Creating a moist environment in the wound. Use specialized absorbent dressings that maintain optimal moisture levels and promote wound healing in diabetics.
Reliable fixation of the bandage. The final stage is the use of an adhesive or polyurethane dressing to protect the wound from external factors and maintain the necessary microclimate for healing
Controlling blood sugar levels
Lubricating the feet with antifungal ointment for prevention after visiting a swimming pool, bath or sauna
It is also necessary to pay special attention to careful nail care, file them down and not cut them with scissors.
Our doctors
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Price
Answers to popular questions
When is it necessary to contact a surgeon?
How to use baneocin-based ointment and hydrogen peroxide?
It is recommended to use an ointment based on baneocin to treat purulent wounds in diabetes mellitus 2 times a day, applying a thin layer of the product to a previously cleaned wound.
Hydrogen peroxide can be used to cleanse affected areas. However, it is important to use the product with caution, as large dosages harm healing tissues. Typically, hydrogen peroxide is applied to the wound, then allowed to dry, and then baneocin ointment is used. Then a sterile dressing is applied to the wound.
What to do if there are no absorbent dressings?
How to care for the amputation site?



















About the disease
Wound treatment for diabetes is a complex of therapeutic and preventive measures. They are aimed at cleansing, healing and restoring the integrity of the skin and underlying tissues of the foot, damaged as a result of neuropathic disorders due to diabetes mellitus.
Approximately 8-10% of people suffering from this disease experience pathological changes in the feet, and about 50% of patients are at risk of developing such complications.