Transcutaneous oximetry (transcutaneous oxygen tension monitoring)
Measuring transcutaneous oxygen tension (TcpO2) is a method that allows you to assess skin oxygenation and blood microcirculation in the extremities. The percutaneous approach allows us to determine the condition of peripheral vessels and diagnose vascular disorders, including diabetic foot syndrome.

specialists

equipment

treatment
Indications for using the method
The transcutaneous oxygen tension (TcpO2) method allows you to assess the level of O2 saturation in the skin. This indicator is an indicator of the condition of peripheral vessels.
This method is also used to determine the need for amputation. This is relevant for critical ischemic syndrome.

Transcutaneous monitoring is also carried out for the purpose of:
- Predicting wound healing The study of oxygen tension is actively used to determine the healing potential of trophic ulcers and extensive wounds in conditions of impaired blood supply.
- Estimates of the effectiveness of vasodilators Transcutaneous oximetry helps evaluate how effectively medications dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
According to doctors, this method is valuable. Its main advantage is its non-invasiveness. This method is safe, including for those who suffer from chronic diseases.
The main disadvantage of the method is its sensitivity to conditions. The accuracy of measurements is sometimes compromised by environmental factors. Another disadvantage is data limitations. Their data quality may vary depending on the individual characteristics of the patient's body. In particular, oxygen transport is affected by the presence of glycated hemoglobin.

Our doctors
Make an appointment at a convenient time on the nearest date

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings, a large number of requests from this site, and in the absence of critical violations.

This award is given to clinics with the highest ratings according to user ratings. It means that the place is known, loved, and definitely worth visiting.

The ProDoctors portal collected 500 thousand reviews, compiled a rating of doctors based on them and awarded the best. We are proud that our doctors are among those awarded.
Price
About the Department of Endocrinology





Reviews 6






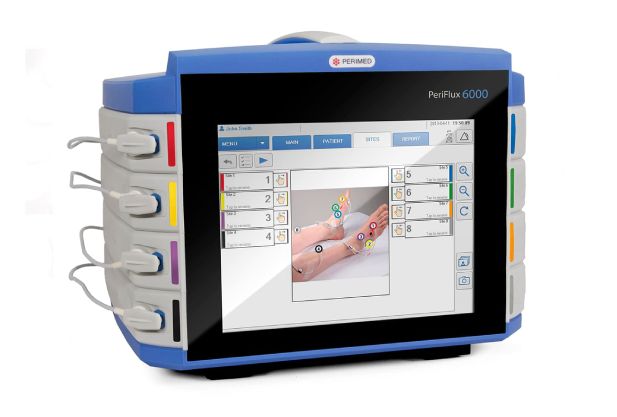















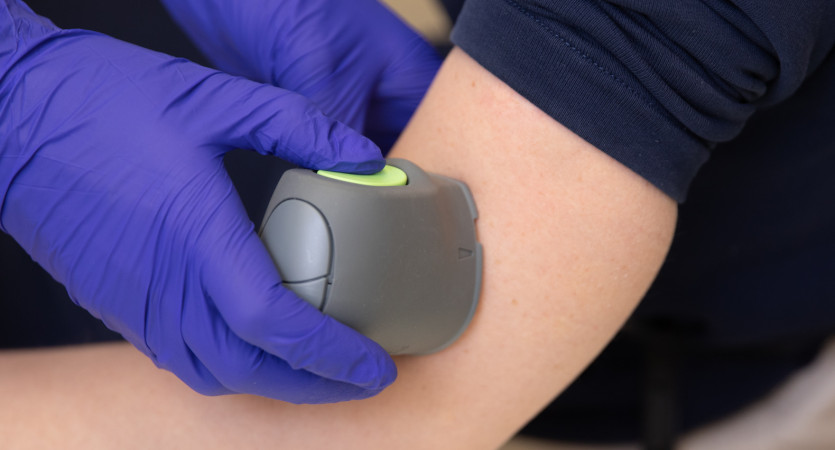
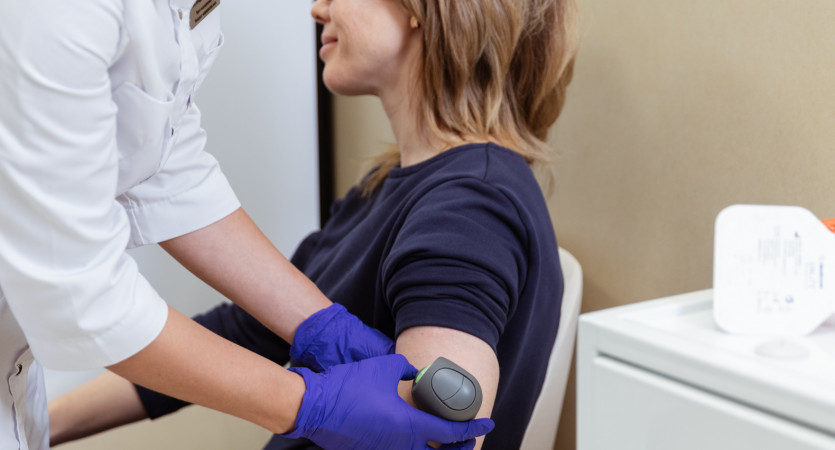










Name and essence of the method
Transcutaneous oxygen tension (transcutaneous or transdermal oximetry) is a non-invasive method. It allows you to assess how well the tissues of the foot are saturated with oxygen.
Transcutaneous monitoring is widely used in various medical fields, including purulent, vascular, and plastic surgery. In anesthesiology and resuscitation, it is relevant for patients who require constant monitoring of oxygen and carbon dioxide.