 TORCH infections are a complex of diseases that negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fruit. Some bacterial and viral pathologies that evolve during gestation have a negative impact not only on women ' s reproductive system but also on embryogenes in general. There is therefore an increasing likelihood that the fruit or its vices will be conquered.
TORCH infections are a complex of diseases that negatively affect the intrauterine development of the fruit. Some bacterial and viral pathologies that evolve during gestation have a negative impact not only on women ' s reproductive system but also on embryogenes in general. There is therefore an increasing likelihood that the fruit or its vices will be conquered.
What are the diseases of TORCH infections?
The word TORCH (TORC) is based on the reduction of the names of common infections. In medical circles, the term " intrauterine infections " is synonymous with " TORCH infections " . Bacterial and viral genes are among the most dangerous diseases for the development of the child:
- T - toxoplasmosis;
- O - other infections (other infections): wind, hepatitis B and C, syphilis, etc.;
- R - rubella
- C - cytomegalovirus (Citomegalovirus);
- H - herpes simplex virus.
In order to prevent the development of pathologies in the child ' s possession, an analysis of the above infections is desirable at the stage of pregnancy planning. Some of them are symptomless, so the examination is necessary even if there is no visible deterioration of health.
TORCH infection analysis
Diagnostics should be held between 1 and 2 months before the intended conception or the first two weeks after the pregnancy. Laboratory studies are carried out once at the time the future mother is registered in a women ' s consultation. The biochemical analysis of the blood can determine the antibodies content of hazardous diseases.
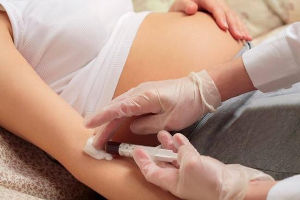 In the case of serum contamination, so-called IgM anthyl is detected, with a maximum concentration at the end of the first month after infection. Immunoglobulin levels have declined sharply in 2-3 months later, so it is almost impossible to identify them.
In the case of serum contamination, so-called IgM anthyl is detected, with a maximum concentration at the end of the first month after infection. Immunoglobulin levels have declined sharply in 2-3 months later, so it is almost impossible to identify them.
Class IgG antilites are detected in plasma 14-20 days after entering disease bacteria and viruses. Immunoglobulin is peaked four weeks later by IgM anteel. Their level is subsequently reduced, but a small part of the immunoglobulin is still determined when the patient is re-examined.
Calculation of analyses
Diagnostics are intended to define antibodies for intrauterine infections. They are protein compounds that are synthesized in response to the infiltration of disease viruses or bacteria. Two types of immunoglobulin - IgG and IgM are identified in the blood analysis.
During the patient survey, 8 different tests are used to identify antibodies to:
- Rubella virus
- Human betaherpesvirus
- Toxoplasma gondii;
- Herpes simplex.
- Varicella Zoster.
The presence of IgG immunoglobulins indicates the acute duration of the infectious disease. In order to determine the approximate time of infection, the results of the IgG antibodies test should be compared.
The discovery of the IgM immunoglobuline signals that immunity had previously been " met " with the instigators of that type and had developed antibodies. Laboratory conditions define qualitative and quantitative indicators for each type of intrauterine infection.
Example of the transcription of the results of the TB tests:
| IgG | IgM | Encryption |
| + | ♪ | The immune system had previously been attacked and immune to infection, so there was no danger to the intrauterine development of the fruit. |
| ♪ | + | The infection has recently occurred, the organism has no immunity to this type of injector. |
| + | + | Disease is in an acute stage of development, so the risk of intrauterine infection is very high. |
| ♪ | ♪ | There is no immunity for the injector, which increases the risk of primary infection during the period of gestation |
Once the results of the tests have been obtained, doctors assess the likelihood of a patient ' s and foetus disease. Medical treatment with anti-microbial and antiviral means is provided for diagnosis of diseases.
Effects of trade
 The primary infection of the mother ' s TORCH infection is a particular danger to the future child. When antibodies are available to disease-producing people, women can easily plan their conception and pregnancy without fear of complications. The absence of immunity to diseased micro-organisms is a reason for preventive measures aimed at reducing the likelihood of infection.
The primary infection of the mother ' s TORCH infection is a particular danger to the future child. When antibodies are available to disease-producing people, women can easily plan their conception and pregnancy without fear of complications. The absence of immunity to diseased micro-organisms is a reason for preventive measures aimed at reducing the likelihood of infection.
Complications and the extent of their expression are defined by the type of disease:
- Toxoplasmosis results in the loss of embryo at an early stage or the development of endocrine pathologies, neurosensor carnage at a later stage of pregnancy;
- The redhead is causing damage to cardiovascular, urea, visual, nervous and digestive systems;
- Herpes - increases the likelihood of absorption or premature birth in recent weeks of pregnancy, violates the functions of liver, spleen and CNS;
- Citomegalovirus increases the likelihood of birth, hepatitis, lung inflammation, heart defects;
- Windspray results in limb underdevelopment, loss of foetus or disruption of visual system functions.
Intrauterine infections in the first months after conception are the most serious complications, ignorance, miscarriage, damage to the nervous tube, etc. If primary infection occurs in the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, the risk of neurological damage to the CNS of the child increases.
Conclusion
In connection with the development of life-threatening complications, TORCH infections are treated in hospital. The timely adoption of ethotropic therapy prevents organism intoxication and penetration of pathogens in the morning of the mother.
div id="nap_form_footer" style="margin-top: 40px;"state == sync, corrected by elderman == @elder_man == sync, corrected by elderman == @elder_man == sync, corrected by elderman == @elder_man Any questions? PER/div constituent == sync, corrected by elderman == @elder_man We're happy to answer them. PER/div constituent " : PER/div constituent duct/section constituent PER/div constituent == sync, corrected by elderman == @elder_man $(document).ready(function(){ If('*[data-fancybox="form-nap"]'.length constituent0) $('#nap_form_footer. ♪ ♪ PER/script