Causes
Symptoms of sphenoiditis
Diagnostics
Sphenoiditis treatment
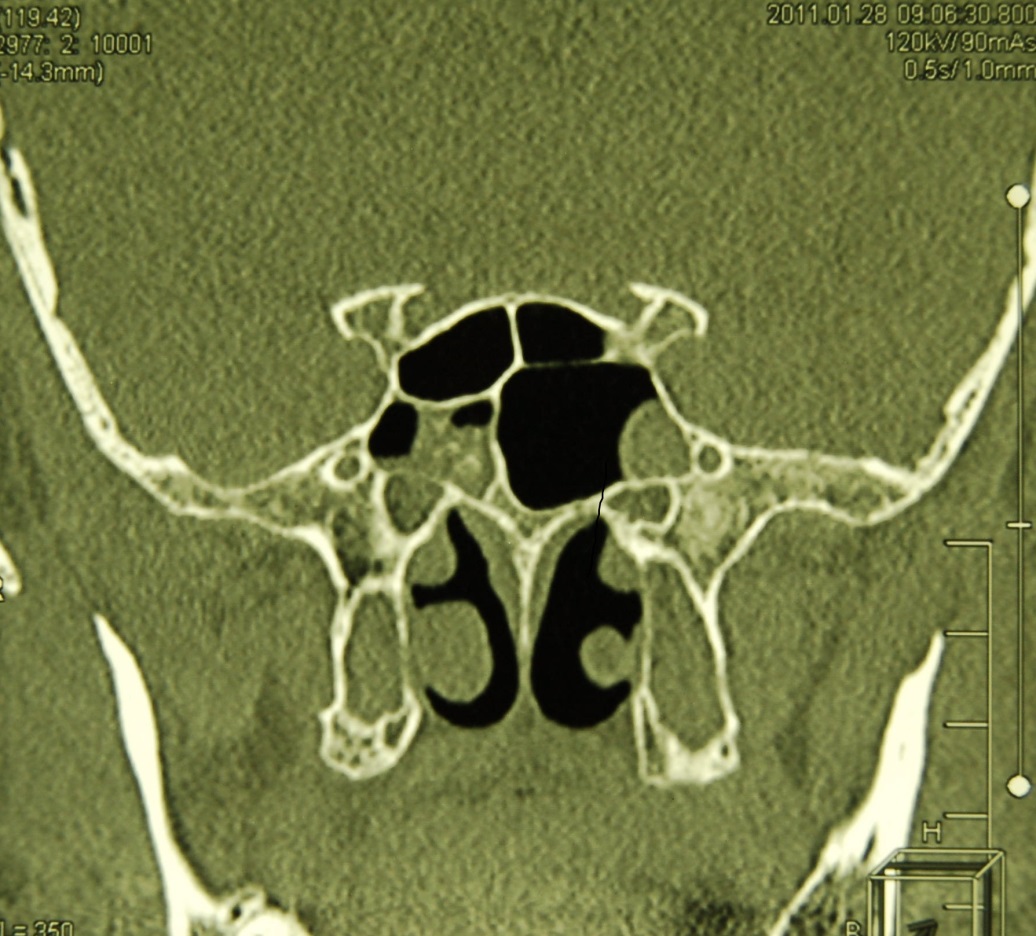 Sphenoiditis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
Sphenoiditis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the sphenoid sinus.
The sphenoid sinus (main) is located deep in the nasal cavity near the base of the skull at the border with the pituitary gland, optic nerves and carotid arteries. This is why certain forms of sphenoiditis can lead to serious complications. Sphenoiditis can be acute or chronic. Since a person has two sphenoid sinuses, then, respectively, the disease can be one or two-sided.
Causes
The development of sphenoiditis occurs as a result of inflammation of the mucous membrane due to its defeat by viruses, bacterial or fungal infection in the presence of the following factors:
- Disruption of the drainage function of the anastomosis of the sphenoid sinus, which leads to its complete isolation and the creation of excellent conditions for the growth of microorganisms
- Foreign bodies entering the sinus during inhalation (if the sinus has a very large anastomosis)
- Narrow and small size of the sphenoid sinus or the presence of additional septa in it
- Chronic diseases of the nose and paranasal sinuses, involving the process and the sphenoid sinus
Most often, the appearance of the disease is facilitated by a combination of several of the listed factors.
Symptoms of sphenoiditis
The main symptom of sphenoiditis is headache. Most often, patients notice pain in the back of the head, as well as in the crown, temples, and eye sockets. The pain is not localized, but a diffuse aching character and does not go away when taking painkillers. Casco-like headache is characteristic. It is also possible the appearance of ophthalmic symptoms - diplopia, decreased visual acuity. Purulent or mucous discharge is also possible, flowing down the back of the pharynx. The patient feels the accumulation of secretions in the nasopharynx, there is an unpleasant taste and odor from the mouth. Some symptoms of the disease can be pronounced, others are absent altogether. The final diagnosis is formed on the basis of a detailed otorhinolaryngological examination.
Diagnostics
Even 30 years ago, the sphenoid sinus was called "forgotten". This was due to the lack of adequate methods for examining the sphenoid sinus. However, nothing stands still, and today the Department of Otorhinolaryngology of the Clinic + 31 has absolutely everything for the diagnosis of sphenoiditis. To confirm the diagnosis, we carry out:
- detailed consultation of a specialist with a patient, aimed at identifying the details of the course of the disease
- otorhinolaryngological examination
- endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx
- computed tomography and radiograph
- if necessary, specialists from the Department of Ophthalmology and Neurology are involved in the examination
Sphenoiditis treatment
Treatment of acute sphenoiditis is aimed at suppressing inflammation and improving outflow from the sphenoid sinus. The patient is prescribed vasoconstrictor nasal drops, drugs to thin the discharge and antibacterial drugs. In addition, the doctor conducts anemization of the nasal cavity in the area of the spheno-ethmoidal pocket in order to improve the outflow from the sphenoid sinus. Sphenoiditis is treated strictly under the supervision of a physician. After the elimination of the acute inflammatory process, a thorough analysis of the causes that contributed to the development of sphenoiditis and their obligatory elimination is necessary.
Improper treatment of acute sphenoiditis can lead to the transition of the disease into a chronic form. Therefore, even in the event of mild symptoms of discomfort in the depths of the nose, one should seek help from an ENT.
Treatment of chronic sphenoiditis usually consists of an operation. Depending on the cause of the development of the process, the natural anastomosis is expanded, the pathological contents are removed, and the anatomy of the spheno-ethmoidal pocket is normalized.
In Clinic + 31, the surgical treatment of chronic sphenoiditis is performed according to the FESS method. Modern equipment allows you to fully control the operation process and carry out precise manipulations in a confined space.
In all cases, timely seeking help is important for the treatment of sphenoiditis. This will help not only speed up the healing process, but also avoid many complications.
Recently, a new BSP technology has appeared in our arsenal - balloon sinusoplasty - which is a set of endoscopic catheter instruments designed to expand the closed fistulas of the paranasal sinuses. These devices can be used both in conjunction with drug treatment and in the framework of traditional surgical techniques used in FESS, including in some cases of sphenoiditis.
